Setting the IDMTL Overcurrent Protection
The IDMTL overcurrent protection Digital Module can be used to improve selectivity with upstream overcurrent protection provided by a fuse or standalone relay, for example, a medium voltage relay, without affecting selectivity with downstream low voltage devices.
Fuses and standalone relays often provide tripping curves which are different from the standard tripping curve offered by MicroLogic X long-time overcurrent protection. The setting guidelines give an indication of how the IDMTL tripping curves can be used to maintain improved selectivity with upstream devices.
Selectivity with Upstream Fuse Using HVF Tripping Curve
The following graph shows how the IDMTL HVF curve can be used to curtail the standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve to help improve selectivity with an upstream fuse.
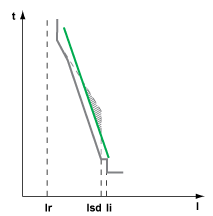
 Upstream fuse tripping curve
Upstream fuse tripping curve
 Compromised selectivity with standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve
Compromised selectivity with standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve
 Tripping curve with IDMTL HVF tripping curve
Tripping curve with IDMTL HVF tripping curve
The following settings are recommended for the IDMTL overcurrent protection:
|
Setting |
Value |
|---|---|
|
IDMTL mode |
ON |
|
IDMTL action |
Trip |
|
IDMTL inhibit |
OFF |
|
IDMTL Ir |
1.0 x In(1) |
|
IDMTL tr |
1 s(1) |
|
IDMTL curve |
HVF |
|
IDMTL reset time type |
Definite time |
|
IDMTL reset time |
0 s |
|
(1) The setting proposed is consistent with commonly used high voltage fuses. The setting should be checked on a case-by-case basis. |
|
The following settings are recommended for long-time overcurrent protection:
oIr ≤ Iz cable
otr = 24 s
NOTE: I2t OFF is recommended for short-time overcurrent protection. With I2t ON the long-time protection could trip faster than the short-time protection.
Selectivity with Upstream Relay Using DT Tripping Curve
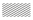
Without IDMTL overcurrent protection, when the MasterPact MTZ circuit breaker is downstream from a relay using a DT tripping curve, it would be necessary to drastically reduce the long-time overcurrent protection time delay, tr, or the short-time overcurrent protection time delay, tsd, to improve selectivity between the devices. The reduction would significantly reduce the setting options for downstream feeders and in some cases, would make downstream selectivity impossible.
The following graph shows how the IDMTL DT curve can be used to curtail the standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve to help improve selectivity with an upstream relay.
 Upstream relay tripping curve
Upstream relay tripping curve
 Compromised selectivity with standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve
Compromised selectivity with standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve
 Tripping curve with IDMTL DT tripping curve
Tripping curve with IDMTL DT tripping curve
The following settings are recommended for the IDMTL overcurrent protection:
|
Setting |
Value |
|---|---|
|
IDMTL mode |
ON |
|
IDMTL action |
Alarm |
|
IDMTL inhibit |
OFF |
|
IDMTL Ir |
≤1.3 Iup |
|
IDMTL tr |
tsd < IDMTL tr ≤ tup -0.2 s |
|
IDMTL curve |
DT |
|
IDMTL reset time type |
Same as reset type of upstream relay |
|
IDMTL reset time |
Lower than reset time of upstream relay |
Selectivity with Upstream Relay Using SIT or VIT Tripping Curve
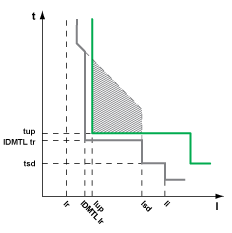
As in the previous example, without IDMTL overcurrent protection, when the MasterPact MTZ circuit breaker is downstream from a relay using an SIT or VIT tripping curve, it would be necessary to drastically reduce the long-time overcurrent protection time delay, tr, or the short-time overcurrent protection time delay, tsd, to improve selectivity between the devices. The reduction would significantly reduce the setting options for downstream feeders and in some cases, would make downstream selectivity impossible.
The following graph shows how the IDMTL SIT or VIT tripping curve can be used to curtail the standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve to help improve selectivity with an upstream relay.
 Upstream relay tripping curve
Upstream relay tripping curve
 Compromised selectivity with standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve
Compromised selectivity with standard long-time overcurrent protection tripping curve
 Tripping curve with IDMTL SIT or VIT tripping curve
Tripping curve with IDMTL SIT or VIT tripping curve
The following settings are recommended for the IDMTL overcurrent protection:
|
Setting |
Value |
|---|---|
|
IDMTL mode |
ON |
|
IDMTL action |
Trip |
|
IDMTL inhibit |
OFF |
|
IDMTL Ir |
≤1.3 Iup |
|
IDMTL tr |
tsd < IDMTL tr ≤ tup @ 6 x Iup |
|
IDMTL curve |
SIT or VIT, same as tripping curve of upstream relay |
|
IDMTL reset time type |
Same as reset type of upstream relay |
|
IDMTL reset time |
Lower than reset time of upstream relay |
NOTE: When the calculated tripping time is lower than tsd, the IDMTL overcurrent protection tripping time is forced to the short-time overcurrent protection tripping time. Setting IDMTL tr > tsd is recommended to avoid a race between short-time overcurrent protection and IDMTL overcurrent protection for currents higher than Isd.
EIT Tripping Curve Application: Pre-alarm for Load-shedding
An example for the application of this tripping curve is as an adjustable pre-alarm for load shedding.
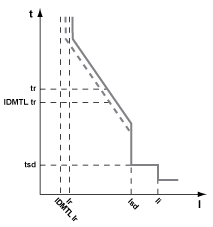
 Tripping curve
Tripping curve
 IDMTL EIT pre-alarm curve
IDMTL EIT pre-alarm curve
The following settings are recommended for the IDMTL overcurrent protection:
|
Setting |
Value |
|---|---|
|
IDMTL mode |
ON |
|
IDMTL action |
Alarm |
|
IDMTL inhibit |
OFF |
|
IDMTL Ir |
0.9 Ir |
|
IDMTL tr |
tsd < IDMTL tr ≤ tr |
|
IDMTL curve |
EIT |
|
IDMTL reset time type |
Inverse time |
|
IDMTL reset time |
10 s |