A Modbus TCP channel must exist.
Configure the Modbus TCP IOScanner
|
Step |
Action |
|---|---|
|
1 |
In the Devices tree, double-click the protocol manager. Result: The configuration window is displayed. |
|
2 |
Select the IOScanner I/O Mapping tab: 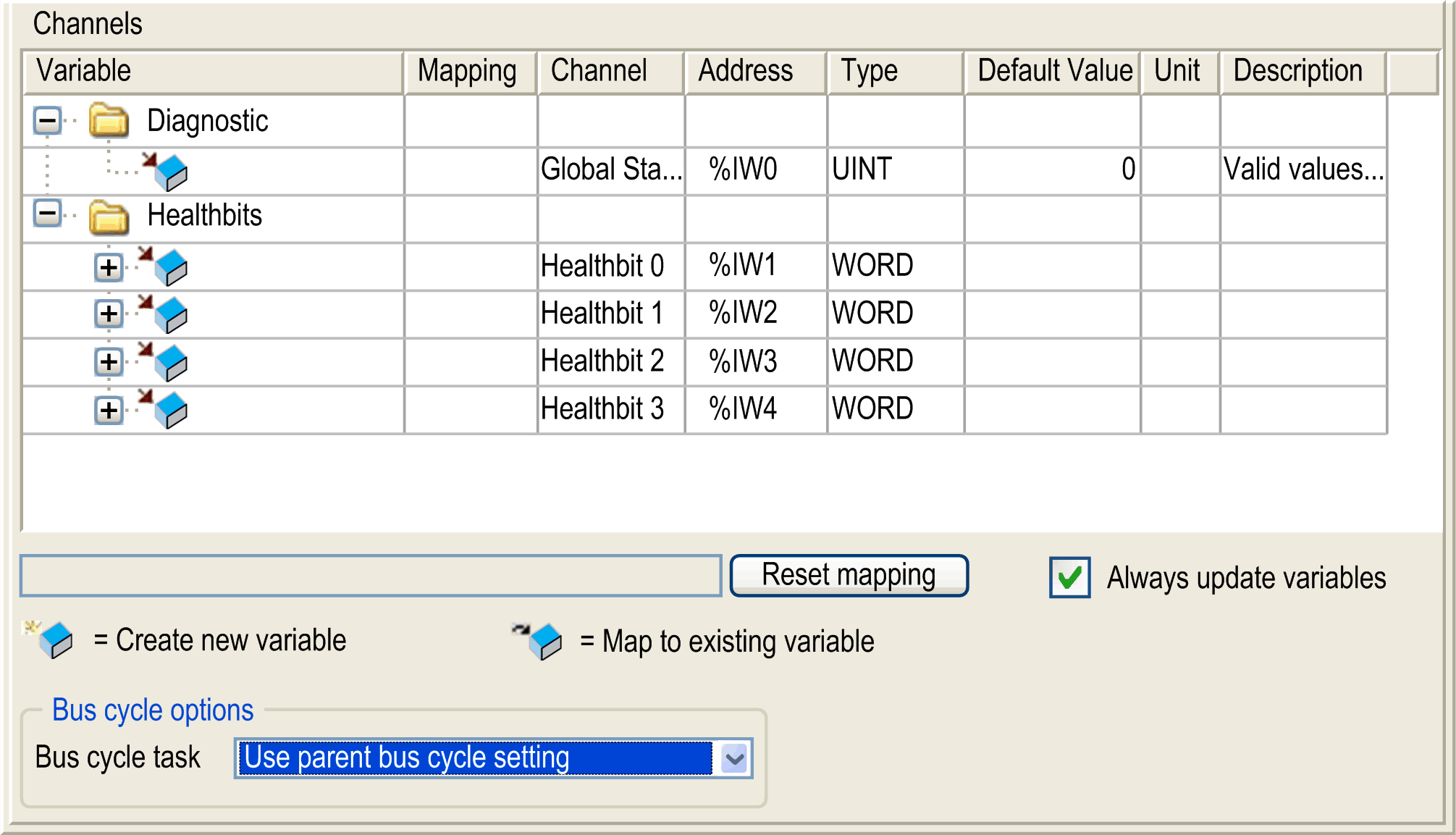
|
|
3 |
Select the Bus cycle task in the list: oUse parent bus cycle setting (by default), oMAST NOTE: The Bus cycle task parameter inside the I/O mapping editor of the device that contains the Modbus TCP IOScanner defines the task responsible for the refresh of the I/O images (%QW, %IW). These I/O images correspond to the Modbus request sent to the Modbus slaves and the health bits. |
|
4 |
Double-click in a cell of the Variable column to open a text field. Enter the name of a variable or click the browse button [...] and chose a variable with the Input Assistant. |
Configure a Modbus TCP Slave Device I/O Mapping
|
Step |
Action |
|---|---|
|
1 |
In the Devices tree, double-click a Modbus TCP slave device. Result: Its configuration window is displayed. |
|
2 |
Select the ModbusTCPSlave I/O Mapping tab. 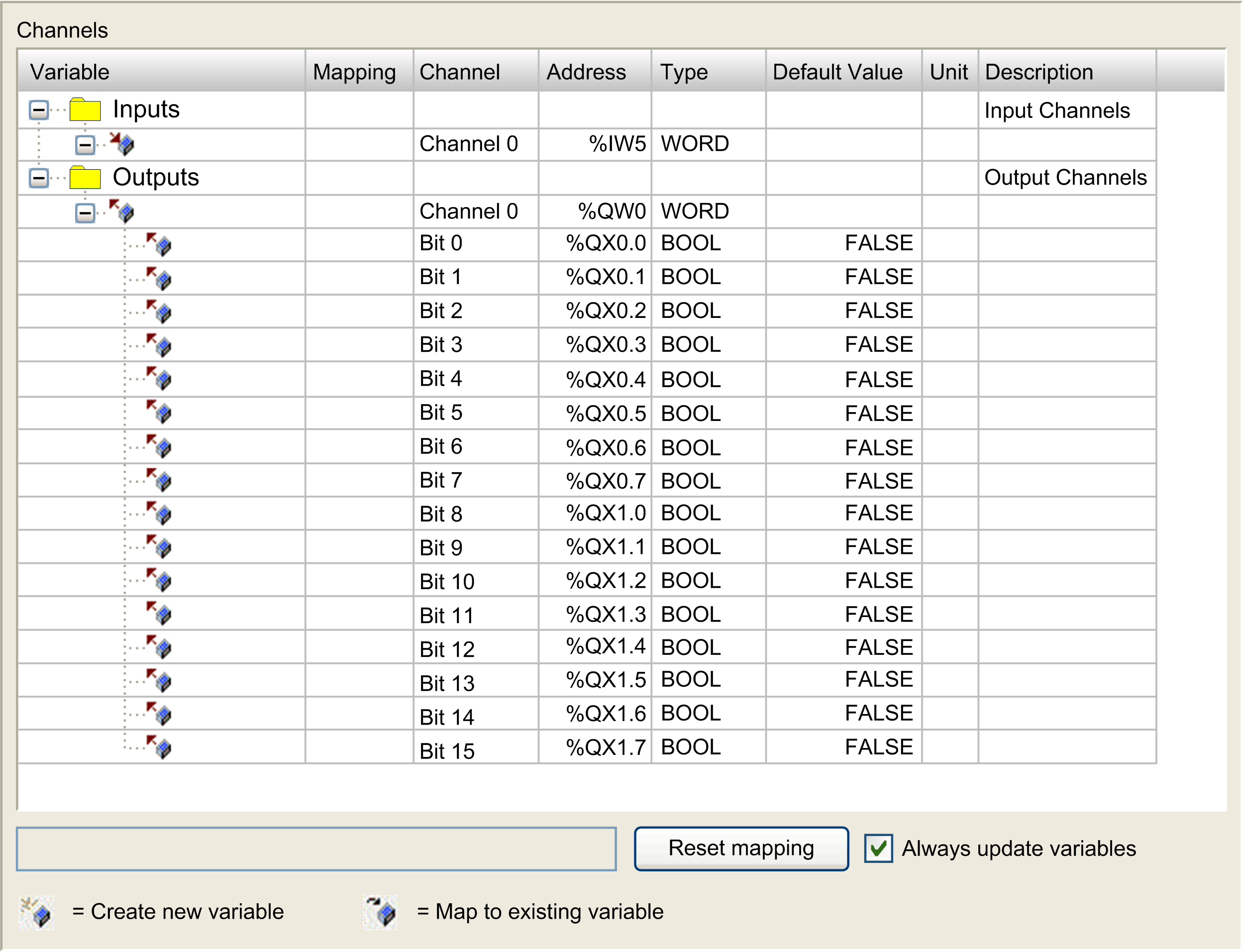
|
|
3 |
Select the Bus cycle task in the list: oUse parent bus cycle setting (by default), oMAST NOTE: The Bus cycle task parameter inside the I/O mapping editor of the device that contains the Modbus TCP IOScanner defines the task responsible for the refresh of the I/O images (%QW, %IW). These I/O images correspond to the Modbus request sent to the Modbus slaves and the health bits. |
|
4 |
Double-click in a cell of the Variable column to open a text field. Enter the name of a variable or click the browse button [...] and chose a variable with the Input Assistant. |