SOS - Safe Operation Stop function
General function description
The SOS function monitors the drive at standstill with active position control (performed by the standard (non-safety-related) controller) and position monitoring (performed by the Safety Module).
The SOS function prevents the motor from deviating more than a defined amount from the stopped position (device parameter SOS_PositionTolerance[sTol] (see below), shown as STol in the graphic below). The drive module provides energy to the motor to enable it to resist external forces.
Monitoring by the safety-related FB/Safety Module
The request of the safety-related function occurs at the beginning of the t1 time interval ('S_SOS_Request' signal in the diagram). t1 is set with the device parameter SOS_StartDelayTime[t1].
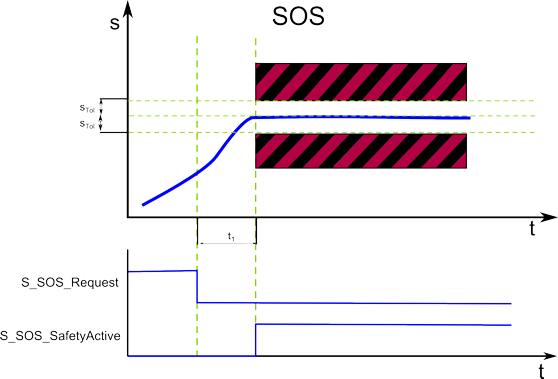
Within the t1 time interval, the standard (non-safety-related) controller also receives the request from the connected process and initiates the motion control function according to the logic and drive parameterization defined in the standard (non-safety-related) application.
After t1 has elapsed, position S0 is captured and SOS is monitored.
SOS performs a safe standstill monitoring. The position control remains in operation. Thus, the motor can deliver full torque to maintain the current position. The actual position will be monitored and must remain within the parameterized position tolerance values (STol).
If the parameterized STol values are not exceeded after t1, the function block switches S_SOS_SafetyActive to SAFETRUE.
Fallback function
If the standstill monitoring detects that the position deviates more than the defined position tolerance from the standstill position (STol in the figure), the STO function is automatically executed as the fallback function.
Application
SOS is useful for applications where machines for specific operations or parts of the machinery must stay at standstill where the drive must provide a holding torque. The method of the drive is to provide power to the motor to counter any torque applied from external forces.
Relevant Safety Module device parameters
How to edit the relevant safety-related device parameters: In the EcoStruxure Machine Expert - Safety 'Devices' window, ...
Left-click the Safety Module in the devices tree.
In the Device Parameterization editor on the right, scroll to the relevant parameter section (see table heading below).
Specify the parameters listed in the table below for this safety-related function.
NOTE:
For the most part, the parameters entered here are monitoring parameters. They define the monitoring behavior and thus determine if a safety-related function is executed as defined or if a fallback function is to be executed due to error detection. The actual drive parameterization (such as deceleration parameters, etc.) is defined by you in EcoStruxure Machine Expert. See topic "Functional description".
For detailed information on the value ranges and default values for these parameters, refer to the corresponding chapter for the safety module used in the "Safety Module Parameters and Process Data Items" guide.
|
Parameter section: Safe_Operating_Stop |
|
|
SOS_StartDelayTime[t1] |
Delay time after which the monitoring of the safety-related function is started. This value must correspond to the time period, the entire motion control system needs to react, i.e., the time after which the standard (non-safety-related) controller is able to initiate the requested safety-related function after receiving the request coded as process data control word via the SERCOS bus. The value set here must be equal or greater than the entire system response time including the standard system response time. The value must not be smaller than the shortest possible total response time of the involved components, i.e., the earliest point in time, when the drive is able to decelerate. |
|
SOS_PositionTolerance[sTol] |
Allowed deviation from the monitored standstill position (STol in the figure above). If the deviation exceeds the defined value, the STO function is activated as the fallback function. |
WARNING
NON-CONFORMANCE TO SAFETY FUNCTION REQUIREMENTS
Verify that the device parameters for the Safety Module correspond to your risk analysis.
Be sure that your risk analysis includes an evaluation for setting incorrectly device parameter values.
Validate the overall safety-related function with regard to the set device parameter values and thoroughly test the application.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage.
Relevant FB inputs/outputs and bit in status word
Function monitoring request via FB input S_SOS_Request = SAFEFALSE
Function status indication via FB output S_SOS_SafetyActive (SAFETRUE = safety-related function activated)
and bit 3 in the DWORD output at AxisStatus (TRUE = safety-related function activated).