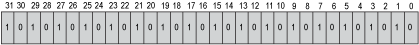
This figure shows the codage rule of the bit position in a DWORD. An example is given for the 16#AAAAAAAA corresponding to the value of 2863311530.
Integer Data Types Description
This table shows the integer data types. Each of the different number types covers a different range types.
|
Type |
Lower limit |
Upper limit |
Memory space |
|---|---|---|---|
|
BYTE |
0 |
255 |
8 Bit |
|
WORD |
0 |
65535 |
16 Bit |
|
DWORD |
0 |
4294967295 |
32 Bit |
|
LWORD |
0 |
264-1 |
64 Bit |
|
SINT |
-128 |
127 |
8 Bit |
|
USINT |
0 |
255 |
8 Bit |
|
INT |
-32768 |
32767 |
16 Bit |
|
UINT |
0 |
65535 |
16 Bit |
|
DINT |
-2147483648 |
2147483647 |
32 Bit |
|
UDINT |
0 |
4294967295 |
32 Bit |
|
LINT |
-263 |
263-1 |
64 Bit |
|
ULINT |
0 |
264-1 |
64 Bit |
REAL/LREAL Data Types Description
This table shows the REAL/LREAL data types. REAL and LREAL are called floating-point types. They are required to represent rational numbers.
|
Type |
Range |
Resolution |
Memory space |
|---|---|---|---|
|
REAL uses 4 bytes |
-3.402e+38...3.402e+38 (-2^128...2^128) |
1,175e-38 (2^-126) |
32 Bit |
|
LREAL uses 8 bytes |
-1.797e+308...1.797e+308 (-2^1024...2^1024) |
2,225e-308 (2^-1022) |
64 Bit |
NOTE: The support of data type LREAL depends on the target device. Please see in the corresponding documentation whether the 64 bit type LREAL gets converted to REAL during compilation (possibility with a loss of information) or persists.