There are different ways to assign the IP address of the module:
oaddress assignment by DHCP server
oaddress assignment by BOOTP server
ofixed IP address
opost configuration file. If a post configuration file exits, this assignment method has priority over the others.
IP address can be changed dynamically:
ovia the Controller Selection tab in EcoStruxure Machine Expert.
NOTE: If the attempted addressing method is unsuccessful, the module will start using a default IP address derived from the MAC address.
Carefully manage the IP addresses because each device on the network requires a unique address. Having multiple devices with the same IP address can cause unintended operation of your network and associated equipment.
|
|
|
UNINTENDED EQUIPMENT OPERATION |
|
oVerify that there is only one master controller configured on the network or remote link. oVerify that all devices have unique addresses. oObtain your IP address from your system administrator. oConfirm that the IP address of the device is unique before placing the system into service. oDo not assign the same IP address to any other equipment on the network. oUpdate the IP address after cloning any application that includes Ethernet communications to a unique address. |
|
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, or equipment damage. |
NOTE: Verify that your system administrator maintains a record of all assigned IP addresses on the network and subnetwork, and inform the system administrator of all configuration changes performed.
The different types of address systems for the controller are shown in the following diagram:

NOTE: If a device programmed to use the DHCP or BOOTP addressing methods is unable to contact its respective server, the module uses the default IP address. It will, however, constantly repeat its request.
The IP process automatically restarts in the following cases:
oController reboot
oEthernet cable reconnection
oApplication download (if IP parameters change)
oDHCP or BOOTP server detected after a prior addressing attempt was unsuccessful.
In the Devices tree, double-click COM_Bus > TM4ES4:
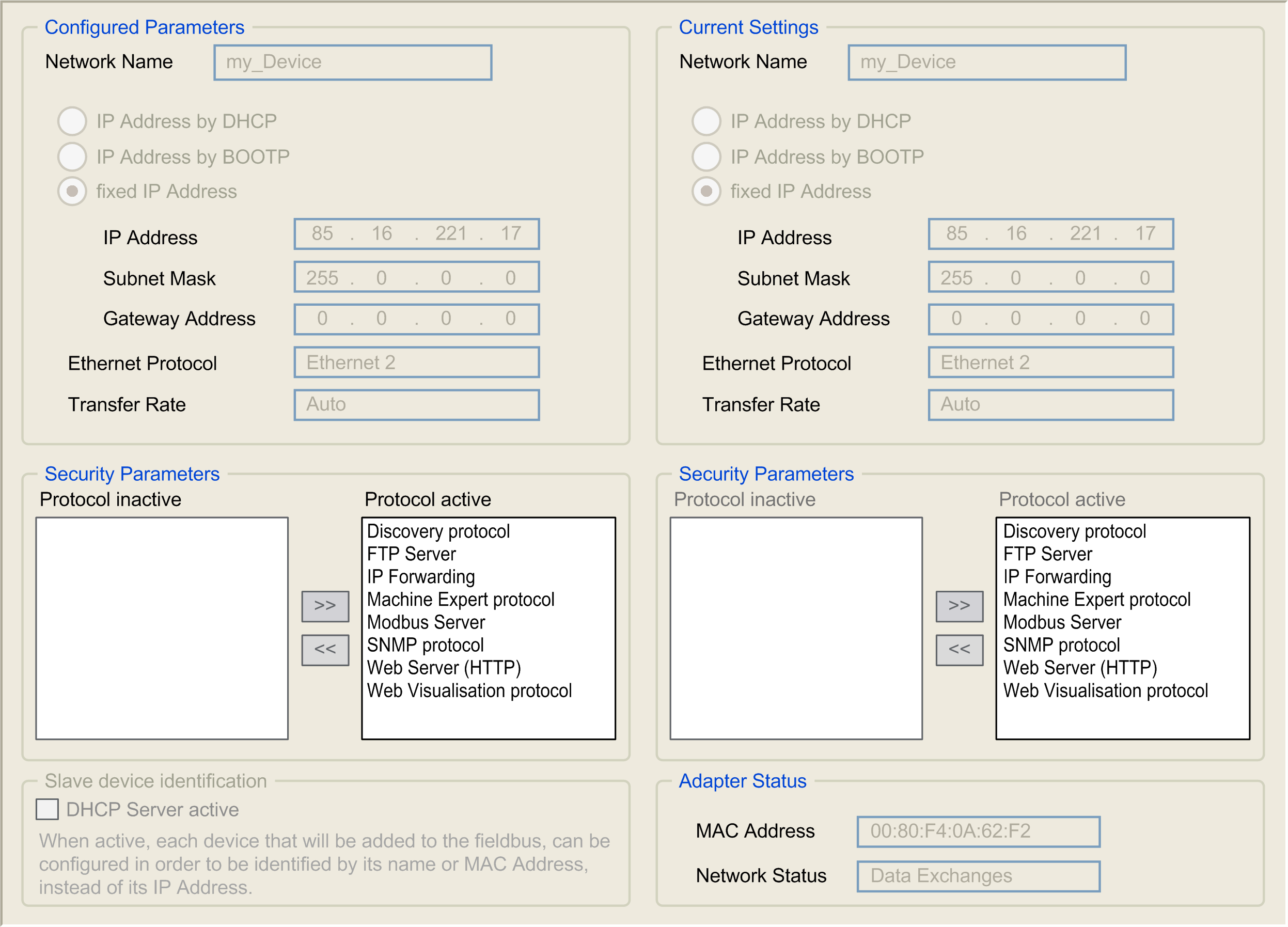
Note: If you are in online mode, you see the two windows. You cannot edit them. If you are in offline mode, you see the Configured Parameters window. You can edit it.
The configured parameters are explained as below:
|
Configured Parameters |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Network Name |
Used as device name to retrieve IP address through DHCP, maximum 16 characters |
|
|
IP Address by DHCP |
IP address is obtained via DHCP. |
|
|
IP Address by BOOTP |
IP address is obtained via BOOTP. |
|
|
Fixed IP Address |
IP address, subnet mask and gateway address are defined by the user. |
|
|
Ethernet Protocol |
Protocol type used (Ethernet 2) |
|
|
Transfer Rate |
Transfer rate and direction on the bus are automatically configured. |
|
|
Security Parameters |
||
The IP address by default is 11.11.x.x.
The last 2 fields in the default IP address are composed of the decimal equivalent of the last 2 hexadecimal bytes of the MAC address of the module.
The MAC address of the module can be retrieved at the bottom of the front face of the module.
The default subnet mask is 255.0.0.0.
NOTE: A MAC address is always written in hexadecimal format, and an IP address in decimal format. You must convert the MAC address to decimal format.
Example: If the MAC address is 00.80.F4.01.80.F2, the default IP address is 11.11.128.242.
NOTE: To take into account the new IP address after the download of a project, reboot the controller by doing a power cycle.
The subnet mask is used to address several physical networks with a single network address. The mask is used to separate the subnetwork and the device address in the host ID.
The subnet address is obtained by retaining the bits of the IP address that correspond to the positions of the mask containing 1, and replacing the others with 0.
Conversely, the subnet address of the host device is obtained by retaining the bits of the IP address that correspond to the positions of the mask containing 0, and replacing the others with 1.
Example of a subnet address:
|
IP address |
192 (11000000) |
1 (00000001) |
17 (00010001) |
11 (00001011) |
|
Subnet mask |
255 (11111111) |
255 (11111111) |
240 (11110000) |
0 (00000000) |
|
Subnet address |
192 (11000000) |
1 (00000001) |
16 (00010000) |
0 (00000000) |
NOTE: The device does not communicate on its subnetwork when there is no gateway.
The gateway allows a message to be routed to a device which is not on the current network.
If there is no gateway, the gateway address is 0.0.0.0.
|
Security Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Machine Expert protocol |
Allows you to deactivate the Machine Expert protocol on Ethernet interfaces. When deactivated, every Machine Expert request from every device will be rejected, including those from the UDP or TCP connection. This means that no connection is possible on Ethernet from a PC with Machine Expert, from a HMI target that wants to exchange variables with this controller, from an OPC server, or from Controller Assistant. |
|
Modbus Server |
Allows you to deactivate the Modbus Server of the logic controller. When deactivated, every Modbus request to the Logic Controller is ignored. |
|
Web Server |
Allows you to deactivate the Web Server of the logic controller. When deactivated, every HTTP request to the logic controller Web server is ignored. |
|
FTP Server |
Allows you to deactivate the FTP Server of the logic controller. When deactivated, every FTP request is ignored. |
|
Discovery protocol |
Allows you to deactivate Discovery protocol. When deactivated, every Discovery request is ignored. |
|
SNMP protocol |
Allows you to deactivate SNMP server of the logic controller. When deactivated, every SNMP request is ignored. |
|
WebVisualization protocol |
Allows you to deactivate the Web visualization pages of the logic controller. When deactivated, every HTTP requests to the logic controller Webvisualisation protocol is ignored. |
|
IP Forwarding |
Allows you to deactivate the IP forwarding service of the logic controller. When deactivated, devices on the device network are no longer accessible from the control network (Web pages, DTM, and so on). |