This system has three linear drives that are in a defined angle to each other. The drives consist of three rails with traversing slides. The tool plate is connected to the traversing slides by connecting rods of the same length. A paired set of connecting rods holds the tool plate parallel to the floor in the same orientation. The kinematics can move the tool plate in three dimensions.
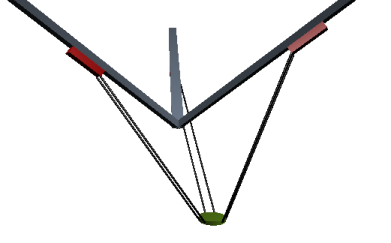
The forward and inverse transformation of these kinematics is calculated in the SMC_Trafo_Tripod_Lin and SMC_TrafoF_Tripod_Lin POUs. The axis angle of the tripod is determined by the angle between the rails and the vertical axis axis (dAxisAngle).
Mechanical requirements, coordinate system
The lengths of the three axes are identical.
The lengths of the connecting rods are identical.
The distance between the pairs of connecting rods to each other is identical for all pairs.
The axis angle between drive rails and the vertical axis is identical for all three drives. The angle can be between 0° and 90°.
The axis defines the movement of the point between the connecting rod joints on the sliders.
The XYZ coordinate system is right-handed. The X and Y vectors are horizontal and Z points up. The origin is defined so that the intersections of the three movement axes with the XY plane (graphics below - points A) is on a circle at position [0,0,0].
Parameterization of the function block "SMC_TrafoF_Tripod_Lin"
|
Name |
Description |
|
dInnerRadius |
Distance from the center of the tool plate to the gripping points of the connecting rods
|
|
dOuterRadius |
|
|
dLength |
Length of the connecting rods |
|
dDistance |
Distance of the pairs of connecting rods to each other |
|
dRotationOffset |
Point A of the first axis defines the X axis by default. With the offset, the construction can be rotated about the Z axis. In this case, point A is no longer on the X axis.
|
|
dOffsetA |
With the offset, the position value of the axis can be set to its basic setting of zero.
|
|
dOffsetB |
|
|
dOffsetC |
|
|
For information, refer to the library description. |
|
See also
This system is a special case of the kinematics described above with the same mechanical requirements. The dAxisAngle between the guide rails and the vertical axis is 0° and the guide rails are parallel to the vertical axis.
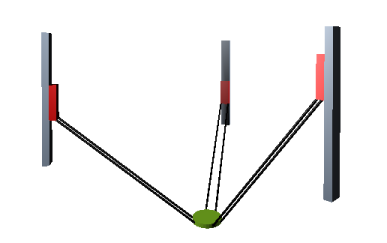
The forward and inverse transformation of these kinematics is calculated in the SMC_Trafo_Tripod_Lin and SMC_TrafoF_Tripod_Lin POUs. The axis angle of the tripod is determined by the angle between the rails and the vertical axis axis (dAxisAngle).
Parameterization of the function block "SMC_TrafoF_Tripod_Lin"
|
Name |
Description |
|
dInnerRadius |
This parameter defines the radius of the circle that is described by the six gripping points of the connecting rods to the tool plate.
|
|
dOuterRadius |
|
|
dLength |
Length of the connecting rods |
|
dDistance |
Distance of the pairs of connecting rods to each other |
|
dRotationOffset |
Point A of the first axis defines the X axis by default. With the offset, the construction can be rotated about the Z axis. In this case, point A is no longer on the X axis.
|
|
dOffsetA |
With the offset, the position value of the axis can be set to its basic setting of zero.
|
|
dOffsetB |
|
|
dOffsetC |
|
|
For information, refer to the library description. |
|
See also
For a tripod, the kinematics are implemented by three rotary drives that are connected to the tool plate by arms and connecting rods.
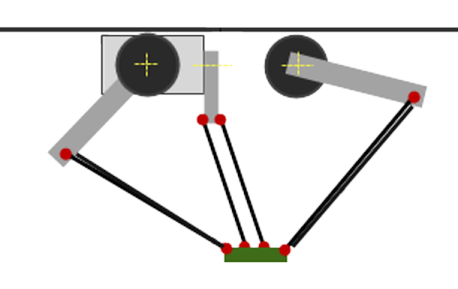
The origin of the coordinate system is the location of the center of the tool plate when all three arms are in a horizontal position.
The forward and inverse transformation of these kinematics is calculated in the SMC_TRAFO_Tripod_Arm and SMC_TRAFOF_Tripod_Arm POUs.
Mechanical requirements, coordinate system
The lengths of the three axes are identical.
The lengths of the connecting rods are identical.
The distance between the pairs of connecting rods to each other is identical for all pairs.
Parameterization of the function block "SMC_TrafoF_Tripod_Arm"
|
Name |
Description |
|
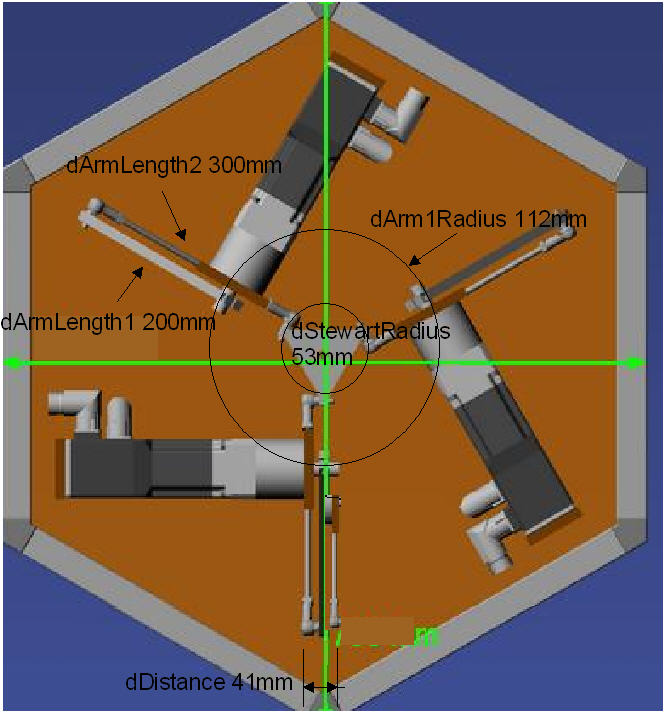
dArmLength1 |
|
|
dArmLength2 |
|
|
dArm1Radius |
This parameter defines the radius of the circle that is described by the three P points.
|
|
dStewartRadius |
This parameter defines the radius of the circle that is described by the six gripping points of the connecting rods to the tool plate.
|
|
dDistance |
Distance of the pairs of connecting rods to each other |
|
dOffsetA |
|
|
dOffsetB |
|
|
dOffsetC |
|
|
For information, refer to the library description. |
|
The following image shows the configuration at position 0 from below:
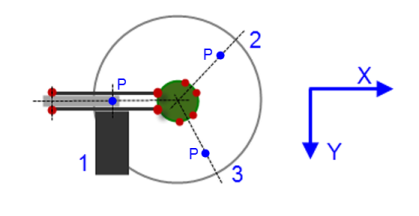
The respective transformations are executed by the following POUs SMC_TRAFO_Tripod_Arm and SMC_TRAFOF_Tripod_Arm:
tta:
SMC_TRAFO_Tripod_Arm := (dArmLength1:=200, dArmLength2:=300, dArm1Radius:=112, dStewartRadius:=53,dDistance:=41,dMaxAngleBallJoint:=60);
ttaf:
SMC_TRAFOF_Tripod_Arm := (dArmLength1:=200, dArmLength2:=300, dArm1Radius:=112, dStewartRadius:=53,dDistance:=41);

See also