SEL
Overview
IEC selection operator for binary selection.
G determines whether IN0 or IN1 is assigned to OUT.
OUT := SEL(G, IN0, IN1) means:
OUT := IN0; if G=FALSE
OUT := IN1; if G=TRUE
Allowed data types:
IN0, IN1, and OUT can be any identical data type. Make sure that variables of the identical data type are used at these positions, especially when using user-defined data types. The compiler verifies the identity of the types and returns compiler errors. Assigning function block instances to interface variables is not supported.
G: BOOL
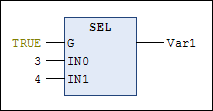
Example in IL
LD TRUE
SEL 3,4 (* IN0 = 3, IN1 =4 *)
ST Var1 (* result is 4 *)
LD FALSE
SEL 3,4
ST Var1 (* result is 3 *)Note
G is TRUE, EcoStruxure Machine Expert does not compute a textual expression that precedes IN0.
When G is FALSE, EcoStruxure Machine Expert does not compute a textual expression that precedes IN1.
In graphical programming languages, where a Box, Jump, Return, Line Branch, or Edge Detection is connected to IN0 or IN1, these statements will always be computed, independently of the input G. This may have an impact on the amount of executed code and thus on the performance. Verify your code carefully to see whether the expressions connected to the inputs IN0 and IN1 should always be executed or only depending on the input G.
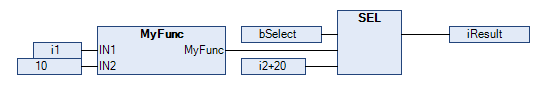
Example 1: MyFunc is directly connected to the input IN1. MyFunc is only executed if bSelect at the input G is FALSE:
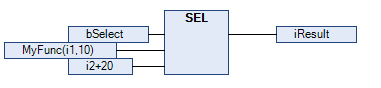
Example 2: MyFunc is connected via a link to the input IN1. MyFunc is always executed (regardless whether bSelect at the input G is FALSE or TRUE):