IP Address Configuration
Introduction
There are different ways to assign the IP address to the added Ethernet interface of the controller:
-
Address assignment by DHCP server
-
Address assignment by BOOTP server
-
Fixed IP address
-
Post configuration file. If a post configuration file exists, this assignment method has priority over the others.
The IP address can also be changed dynamically through the:
-
Communication Settings tab in EcoStruxure Machine Expert
Carefully manage the IP addresses because each device on the network requires a unique address. Having multiple devices with the same IP address can cause unintended operation of your network and associated equipment.
| WARNING | |
|---|---|
Address Management
This diagram shows the different types of address systems for the controller:
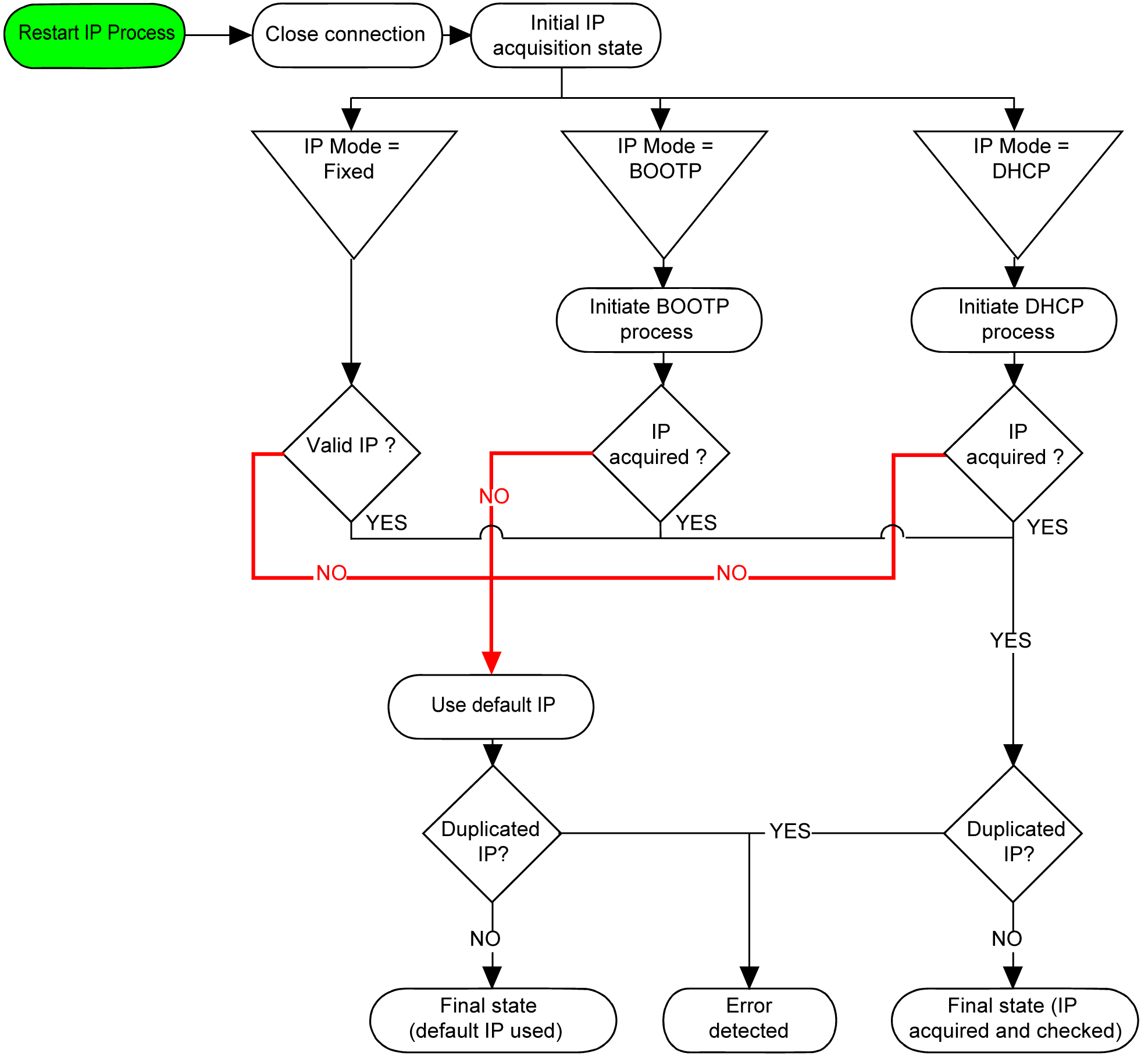
The IP process restarts in the following cases:
-
Controller reboot
-
Ethernet cable reconnection
-
Application download (if IP parameters change)
-
DHCP or BOOTP server detected after a prior addressing attempt was unsuccessful.
Ethernet Configuration
In the , double-click :

Note: If you are in online mode, you see the two windows. You cannot edit them. If you are in offline mode, you see the Configured Parameters window. You can edit it.
This table describes the configured parameters:
|
Configured Parameters |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
Used as device name to retrieve IP address through DHCP, maximum 15 characters. |
|
|
|
IP address is obtained by DHCP server. |
|
|
|
IP address is obtained by BOOTP server. |
|
|
|
IP address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address are defined by the user. |
|
|
|
Protocol type used (Ethernet 2). |
|
|
|
Speed and Duplex are in auto-negotiation mode. |
|
Default IP Address
The default IP addresses are:
-
10.11.x.x. for Ethernet_1
-
10.10.x.x. for Ethernet_2 (only available on TM251MESE)
The last two fields in the default IP address are composed of the decimal equivalent of the last two hexadecimal bytes of the MAC address of the port.
The MAC address of the port can be retrieved on the label placed on the front side of the controller.
The default subnet mask is Default Class A Subnet Mask of 255.0.0.0.
Example: If the MAC address is 00.80.F4.01.80.F2, the default IP address is 10.10.128.242.
Address Classes
The IP address is linked:
-
to a device (the host)
-
to the network to which the device is connected
An IP address is always coded using 4 bytes.
The distribution of these bytes between the network address and the device address may vary. This distribution is defined by the address classes.
The different IP address classes are defined in this table:
|
Address Class |
Byte1 |
Byte 2 |
Byte 3 |
Byte 4 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Class A |
0 |
Network ID |
Host ID |
|||||
|
Class B |
1 |
0 |
Network ID |
Host ID |
||||
|
Class C |
1 |
1 |
0 |
Network ID |
Host ID |
|||
|
Class D |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
Multicast Address |
|||
|
Class E |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
Address reserved for subsequent use |
||
Subnet Mask
The subnet mask is used to address several physical networks with a single network address. The mask is used to separate the subnetwork and the device address in the host ID.
The subnet address is obtained by retaining the bits of the IP address that correspond to the positions of the mask containing 1, and replacing the others with 0.
Conversely, the subnet address of the host device is obtained by retaining the bits of the IP address that correspond to the positions of the mask containing 0, and replacing the others with 1.
Example of a subnet address:
|
IP address |
192 (11000000) |
1 (00000001) |
17 (00010001) |
11 (00001011) |
|
Subnet mask |
255 (11111111) |
255 (11111111) |
240 (11110000) |
0 (00000000) |
|
Subnet address |
192 (11000000) |
1 (00000001) |
16 (00010000) |
0 (00000000) |
Gateway Address
The gateway allows a message to be routed to a device that is not on the same network.
If there is no gateway, the gateway address is 0.0.0.0.
The gateway address can be defined on Ethernet_1 interface. The traffic to unknown networks is sent through this gateway address, or to address configured on IP routing table.
Security Parameters
This table describes the different security parameters:
|
Security Parameters |
Description |
Default settings |
|---|---|---|
|
|
This parameter deactivates Discovery protocol. When deactivated, Discovery requests are ignored. |
Active |
|
|
This parameter deactivates the FTP Server of the controller. When deactivated, FTP requests are ignored. |
Active |
|
|
This parameter deactivates the IP forwarding service of the controller. When deactivated, devices on the device network are no longer accessible from the control network (Web pages, DTM, and so on).
NOTE: This parameter is only available on the Ethernet_1 network.
|
Inactive |
|
|
This parameter deactivates the Machine Expert protocol on Ethernet interfaces. When deactivated, any Machine Expert request from any device is rejected, including those from the UDP or TCP connection. Therefore, no connection is possible on Ethernet from a PC with EcoStruxure Machine Expert, from an HMI target that wants to exchange variables with this controller, from an OPC server, or from Controller Assistant. |
Active |
|
|
This parameter deactivates the Modbus Server of the controller. When deactivated, any Modbus request to the controller is ignored. |
Inactive |
|
|
This parameter deactivates the remote connection. When deactivated, Fast TCP requests are ignored. |
Active |
|
|
This parameter deactivates the Web server of the controller. When deactivated, HTTPS requests to the controller Web server are ignored. |
Active |
|
|
This parameter deactivates the SNMP server of the controller. When deactivated, SNMP requests are ignored. |
Inactive |
|
|
This parameter deactivates the WebVisualisation pages of the controller. When deactivated, HTTP requests to the logic controller WebVisualisation protocol are ignored. |
Inactive |
Slave Device Identification
When is selected, devices added to the fieldbus can be configured to be identified by their name or MAC address, instead of their IP address. Refer to DHCP Server.