ST Editor in Online Mode
Overview
In online mode, the structured text editor (ST editor) provides views for monitoring, and for writing, and forcing the variables and expressions on the controller. Debugging (breakpoints, stepping, and so on) is available. See Breakpoint positions in ST Editor.
-
For information on how to open objects in online mode, refer to the description of the user interface in online mode.
-
For information on how to enter prepared values for variables in online mode, see Forcing of variables.
-
The editor window of an ST object also includes the declaration editor in the upper part. For information on the declaration editor in online mode, see Declaration Editor in Online Mode.
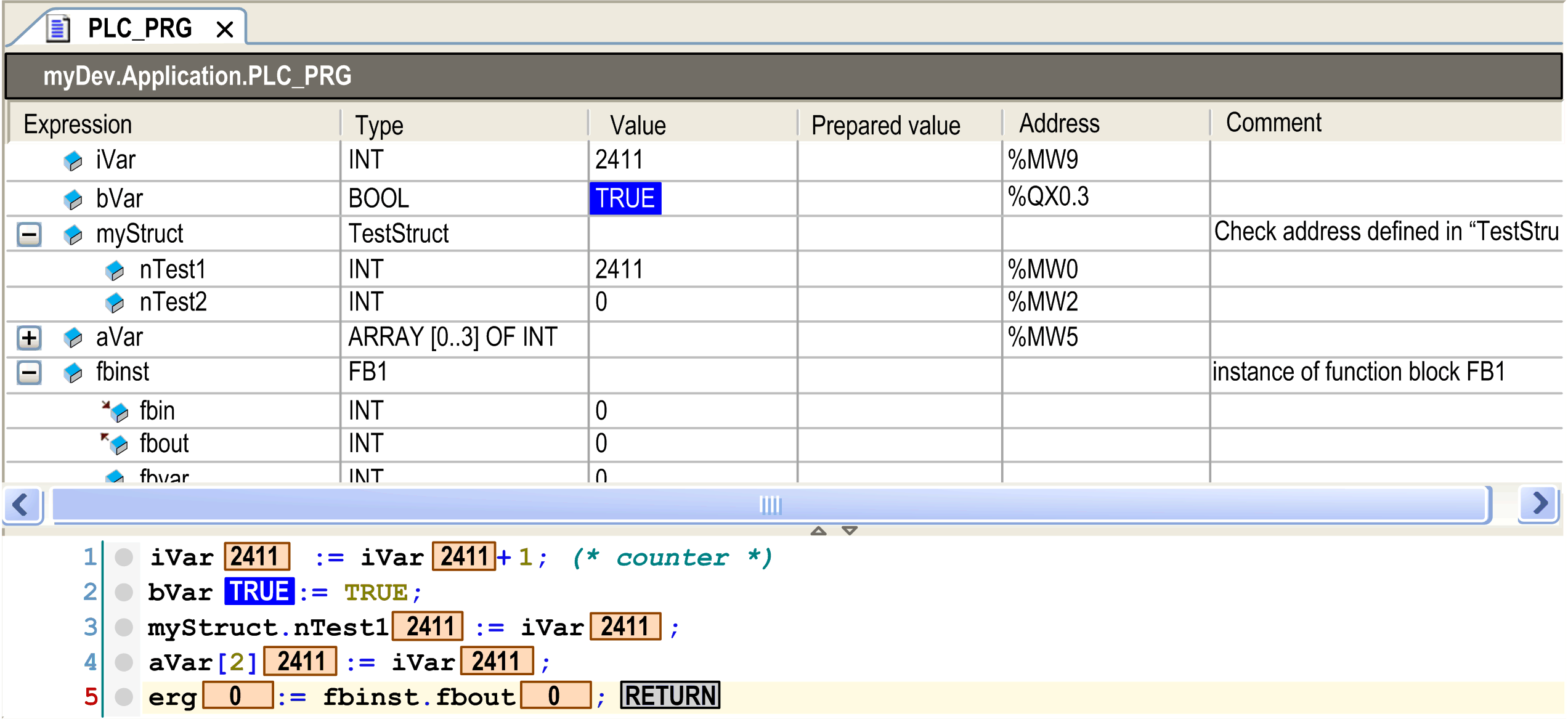
Monitoring
If the option is activated in the tab of the dialog box, small monitoring boxes will be displayed behind each variable showing the actual value.
Online view of a program object PLC_PRG with monitoring:
Forcing of Variables
In addition to the possibility of entering a prepared value for a variable within the declaration of any editor, the ST editor offers double-clicking the monitoring box of a variable within the implementation part (in online mode). Enter the prepared value in the dialog box that appears.
| WARNING | |
|---|---|
Dialog box
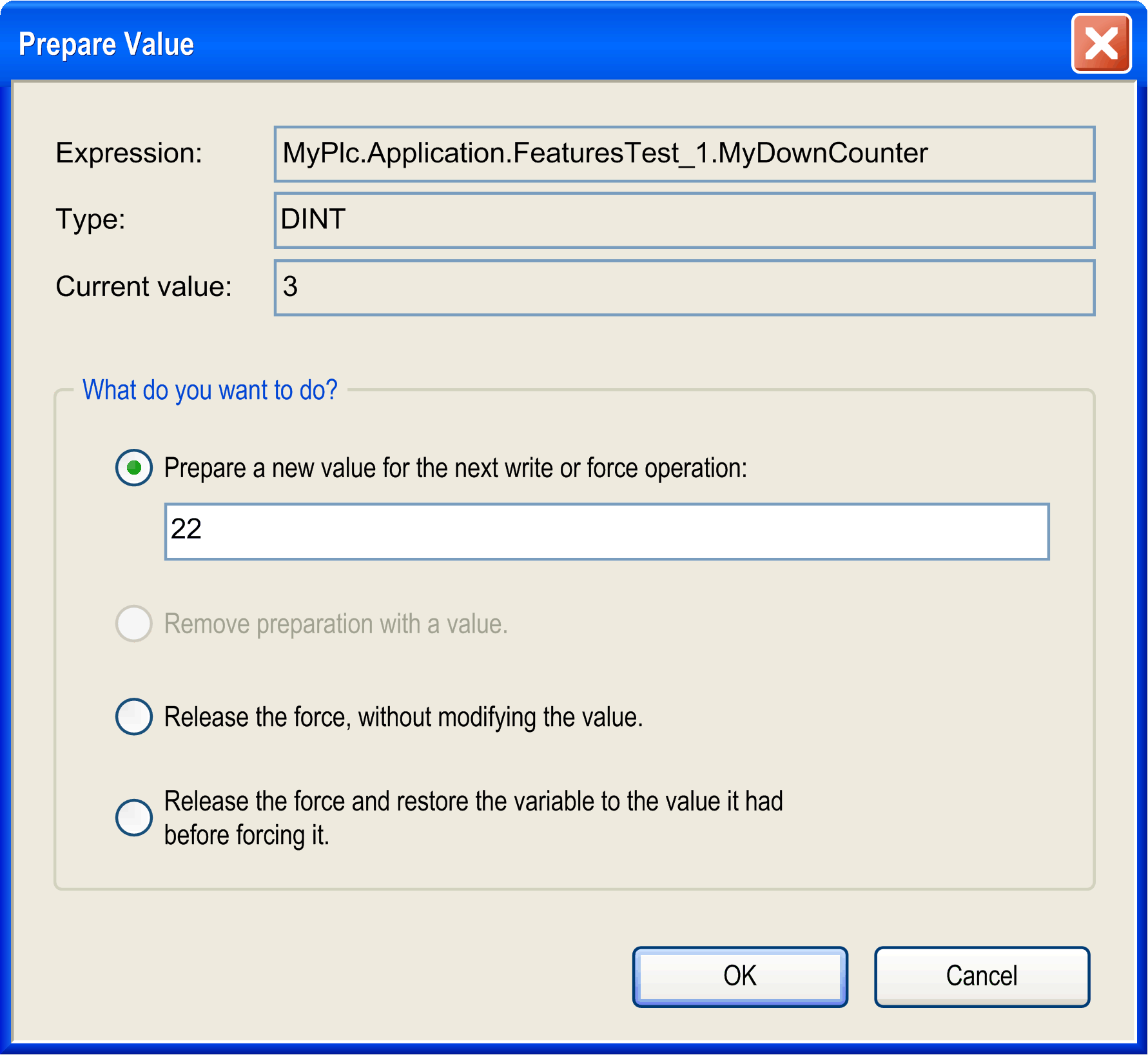
You find the name of the variable completed by its path within the (), its type, and current value.
By activating the corresponding item, you can choose the following options:
-
preparing a new value which has to be entered in the edit field
-
removing a prepared value
-
releasing the variable that is being forced
-
releasing the variable that is being forced and resetting it to the value it was assigned before forcing
To carry out the selected action, execute the command (item ) or press the F7 key.
Breakpoint Positions in ST Editor
You can set a breakpoint basically at the positions in a POU where values of variables can change or where the program flow branches out or another POU is called. In the following descriptions, {BP} indicates a possible breakpoint position.
Assignment:
At the beginning of the line. Keep in mind that assignments as expressions define no further breakpoint positions within a line.
-loop:
-
before the initialization of the counter
-
before the test of the counter
-
before a statement
{BP} FOR i := 12 TO {BP} x {BP} BY 1 DO
{BP} [statement1]
...
{BP} [statementn-2]
END_FOR-loop:
-
before checking the condition
-
before an instruction
{BP} WHILE i < 12 DO
{BP} [statement1]
...
{BP} [statementn-1]
END_WHILEREPEAT-loop:
-
before checking the condition
REPEAT
{BP} [statement1]
...
{BP} [statementn-1]
{BP} UNTIL i >= 12
END_REPEATCall of a program or a function block:
At the beginning of the line.
{{BP} POU( );At the end of a POU:
When stepping through, this position will also be reached after a RETURN instruction.
Breakpoint display in ST
|
Breakpoint in Online Mode |
Disabled Breakpoint |
Program Stop at Breakpoint |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|