Configuring the Fieldbus Interface
Introduction
This section describes the configuration of the Modicon TM5 EtherNet/IP Fieldbus Interface as an Ethernet/IP target device.
For further information about EtherNet/IP, refer to the www.odva.org website.
EtherNet/IP Target Configuration
To configure your TM5NEIP1 as an EtherNet/IP target device, add the fieldbus interface to your project. Refer to Adding a Fieldbus Interface.
Industrial Ethernet Port Configuration
The device can be connected via Industrial Ethernet. For information and procedures necessary to configure the device network, refer to the EcoStruxure Machine Expert EtherNet/IP User Guide.
EtherNet/IP Parameter Configuration
To configure the Ethernet/IP parameters, double-click the TM5 EtherNet/IP Fieldbus Interface node in the .
Target Settings Tab
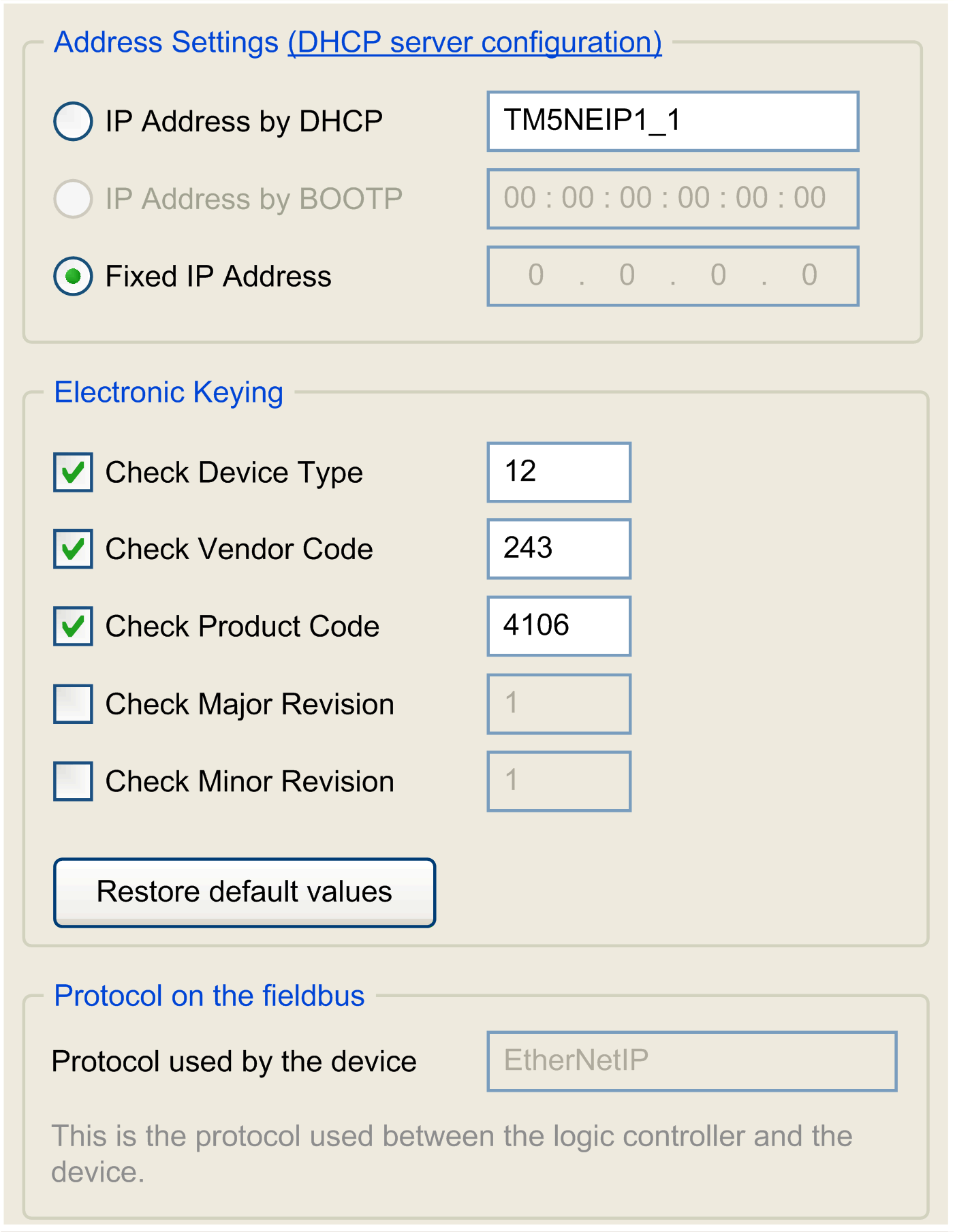
|
|
The configured parameters are explained as below:
|
Configurable Parameters |
Description |
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
IP address is obtained via DHCP |
|
|
|
IP address, subnet mask and gateway address are defined by the user |
|
Electronic Keying
signatures are used to identify the device. is information contained in the firmware of the device (Vendor Code, Product Code, …).When the controller scanner starts, it compares each selected electronic keying value with the corresponding information in the device. If the device values are not the same as the application values, the logic controller no longer communicates with the device.
You can configure any of following attributes:
|
Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The general type of the product. |
|
|
The device manufacture. |
|
|
The specific type of the product. The Product Code maps to a catalog number. The Product Code differentiates the product from other products of the same Device Type under the indicated Vendor. |
|
|
A number that represents the functional capabilities of a device. Typically, a Major Revision is backwards compatible with a lower Major Revision. |
|
|
A number that represents behavior changes in the device, for example, anomaly corrections. This number does not represent the functional capabilities of a device. |
Connections on Ethernet/IP
To access a target device, an Originator opens a connection which can include several sessions that send requests.
One explicit connection uses one session (a session is a TCP or UDP connection).
One I/O connection uses two sessions.
The total number of connections is 32.
Configuration Stream Tab
The following table shows the parameters available in the tab:
|
Parameter name |
Type |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
TM5 Bus |
|||
|
TM5CycleTime |
Enumeration of BYTE |
0: 40000 us |
TM5 link configuration |
|
Communication Loss |
|||
|
CommunicationLossAction |
Enumeration of BYTE |
0: No Action |
Communication interruption (timeout) action |
|
CommunicationLossFieldOfAction |
Enumeration of BYTE |
0: Assembly Local |
Communication interruption (timeout) scope |
|
CommunicationLossResetMode |
Enumeration of BYTE |
0: Exploit via Bus Controller Object, Instance service 32 hex |
Communication interruption (timeout) reset mode |
|
Controller Programming Mode |
|||
|
ProgrammModeAction |
Enumeration of BYTE |
0: No Action |
Program mode (idle) action |
|
ProgramModeFieldOfAction |
Enumeration of BYTE |
0: Assembly Local |
Program mode (idle) scope |
|
Miscellaneous |
|||
|
Webserver |
Enumeration of BYTE |
0: Disabled* |
Enables or disables the web server. |
| (*) Default value. | |||
Connections Tab
Each EtherNet/IP device has connections.
In the , double-click an EtherNet/IP device and select the tab.
|
Column |
Comment |
|---|---|
|
|
The connection number is unique. It is automatically assigned by EcoStruxure Machine Expert. |
|
|
The connection name is generated automatically by EcoStruxure Machine Expert. |
|
|
Requested Packet Interval: The time period between cyclic data transmissions requested by the scanner. |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of bytes to exchange between the Originator (O) and the Target (T). |
|
|
To create a connection, click .
To modify a connection, select a connection and click , or double-click it.
To remove a connection, select a connection and click .
Tab
Variables can be defined and named in the tab. Additional information such as topological addressing is also provided in this tab. For information and procedures necessary to configure the , refer to the EcoStruxure Machine Expert Programming Guide.
Status
The description of the TM5 EtherNet/IP Fieldbus Interface status is as follows:
-
Reads the fieldbus interface status. 32 bits of information are available.
-
Bits 0 to 10 indicate error-free states; bits 11 to 31 indicate error states.
-
Individual states are also indicated by the LED status indicators on the fieldbus interface.
The following table shows bits, their values and description:
|
Bit |
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
00000001 |
The adapter was configured using configuration assemblies. |
|
1 |
00000002 |
System start or I/O module detection is done. |
|
2 |
00000004 |
Fieldbus interface is not ready to start I/O module configuration. |
|
3 |
00000008 |
Fieldbus interface I/O module configuration is in process. |
|
4 |
00000010 |
All I/O module configuration is complete. |
|
5 |
00000020 |
Ethernet/IP stack initialization is done. |
|
6 |
00000040 |
Ethernet/IP stack configuration is done. |
|
7…10 |
00000080...00000400 |
Reserved |
|
11 |
00000800 |
Memory error |
|
12 |
00001000 |
Flash data error while reading the primary flash memory page. |
|
13 |
00002000 |
Firmware update error detected. The fieldbus interface is booting with the default firmware. |
|
14 |
00004000 |
Missing module detected during boot phase |
|
15 |
00008000 |
Incorrect module detected during boot phase. |
|
16 |
00010000 |
The adapter has not yet received an IP address assignment from DHCP. |
|
17 |
00020000 |
2 or more identical IP addresses exist in the network. |
|
18 |
00040000 |
General EIP stack error |
|
19 |
00080000 |
Communication resources: Limit reached |
|
20 |
00100000 |
Stack socket error detected |
|
21 |
00200000 |
Insufficient memory |
|
22 |
00400000 |
Error detected while reading the primary flash memory page. |
|
23 |
00800000 |
Incorrect configuration assembly data |
|
24 |
01000000 |
“Scanner auto-connected” error |
|
25 |
02000000 |
Corrupted firmware detected. The fieldbus interface is booting with the default firmware. |
|
26 |
04000000 |
Error when generating the configuration |
|
27 |
08000000 |
Configuration resource is locked |
|
28…31 |
01000000…80000000 |
Reserved |
You can also read the status information of the remote adapter with the FB_RemoteAdapter function block properties from the TM5BC EtherNetIP Remote Adapter library.
|
Name |
Type |
Initial |
Value name |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Status |
USINT |
0 |
Initializing |
Initialization of the Remote Adapter |
|
1 |
Searching |
Try to get connection to the Remote Adapter |
||
|
2 |
Configuring |
Writing the user parameters |
||
|
3 |
Configured |
Configuration applied successfully |
||
|
4 |
Aborted |
Writing was aborted following the flag AbortIfError |
||
|
5 |
Error |
Error detected (see property Errorinfo for more details) |
||
|
6 |
Disabled |
Remote Adapter is disabled |
The property ErrorInfo is a structure providing details about the error detected:
|
Name |
Type |
Initial |
Value name |
Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
uiErrorNumber |
USINT |
0 hex...255 hex |
CommunicationErrorCodes |
Communication error codes |
|
256 hex... 1000 hex |
OperationErrorCodes |
Operation Error Codes = uiErrorNumber – 256 hex |
||
|
1001 hex |
ConfigurationError |
Configuration of the Remote Adapter not successful or incorrect configuration of the user parameters |
||
|
1002 hex |
EipDataExchUnexpectedOuput |
Unexpected reaction of the function block EipDataExch |
||
|
1003 hex |
EipDataExchTimeoutExpired |
Timeout of the function block EipDataExch |
||
|
1004 hex |
ReadingUserParameterFailed |
Reading a user parameter from the Remote Adapter not successful |
||
|
1005 hex |
TimeoutStartConnection |
Timeout while waiting for the health bit after starting the connections |
||
|
1006 hex... FFFF FFFF hex |
- |
Reserved |
||
|
uiParameterNumber |
USINT |
- |
- |
Number of the parameter implied in the error detected |
Profile
The controller supports the following objects:
|
Object class |
Class ID (hex) |
Number of Instances |
Effect on Interface Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
|
01 |
1 |
Provides general information about the bus coupler. |
|
|
02 |
2 |
Provides message connection. |
|
|
04 |
2 |
Defines I/O data format. |
|
|
06 |
1 |
– |
|
|
64 |
2 |
– |
|
|
F4 |
1 |
Displays connection properties. |
|
|
F5 |
1 |
Displays TCP/IP configuration. |
|
|
F6 |
1 |
Displays counter and status information for the IEEE 802.3 interface. |
Common Class Attributes
The following table describes the class attributes of all supported object:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Get |
UINT |
Object revision |
|
2 |
Get |
UINT |
Largest instance number of the object generated in this class level |
|
3 |
Get |
UINT |
Number of generated instances |
|
4 |
Get |
STRUCT of UINT |
Number of optional attributes |
|
ARRAY of UINT |
List of optional attribute numbers |
||
|
5 |
Get |
STRUCT of UINT |
Number of optional services |
|
ARRAY of UINT |
List of optional service codes |
||
|
6 |
Get |
UDINT |
Largest possible ID number of class attributes |
|
7 |
Get |
UDINT |
Largest possible ID number of instance attributes |
Identity Object (Class ID = 01 hex)
The identity object provides identification and status information about the device or object.
The following table provides a general overview of the identity object:
|
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1, 2, 3, 6, 7 |
Class attributes |
|
1, E |
Class services |
|
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 |
Instance attributes |
|
1, 5, E |
Instance services |
The following table describes the instance attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Get |
UINT |
|
0377 hex (887) |
|
2 |
Get |
UINT |
|
Default value: F3 hex (243) = Adapter device |
|
3 |
Get |
UINT |
|
Hardware ID of the fieldbus interface. This is identical to the first four characters printed on the module's housing. Fieldbus interface code: 100A hex (4106) |
|
4 |
Get |
STRUCT of USINT |
|
ZZ = Firmware major revision |
|
STRUCT of USINT |
|
YY = Firmware minor revision |
||
|
5 |
Get |
WORD |
|
Refer to status code table below. |
|
6 |
Get |
UDINT |
|
Identical to the seven characters on the module's housing after the hardware ID |
|
7 |
Get |
STRING |
|
1C hex (length = 28) and hexadecimal equivalent of TM5 EtherNet/IP Fieldbus Interface TM5NEIP1 |
|
8 |
Get |
USINT |
|
0 = Does not exist 1 = Device self-test 2 = Standby 3 = Operational 4 = Major recoverable error 5 = Major unrecoverable error 6 to 254 = Reserved |
The following table describes the status codes of instance attribute 5:
|
Bit |
Definition |
Function |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
Owned by master (predefined scanner/adapter connection) |
There is an owner for the device or object within the device. In the scanner/adapter paradigm, setting this bit means that a scanner has been assigned to a predefined scanner/adapter connection set. |
|
1 |
- |
Reserved, set to 0 by default. |
|
2 |
Configured |
The firmware is no longer set to the pre-configured default behavior. This does not include how communication is configured. |
|
3 |
- |
Reserved, set to 0 by default. |
|
4…7 |
Extended device status (Refer to extended status codes table below) |
The extended device status indicates whether the device is following the general definition for using this bit through the use of the |
|
8 |
Minor recoverable error |
The device has detected an error that appears to be recoverable. This detected error does not cause the device to enter into an error state. |
|
9 |
Minor unrecoverable error |
The device has detected an error that does not appear to be recoverable. This detected error does not cause the device to enter into an error state. |
|
10 |
Major recoverable error |
The device has detected an error that makes it to enter the "Major recoverable error". |
|
11 |
Major unrecoverable error |
The device has detected an error that makes it to enter the "Major unrecoverable error". |
|
12-15 |
- |
Reserved, set to 0 by default. |
The following table describes the extended status codes of Bits 4-7 of instance attribute 5:
|
Bits 4…7 |
Definition |
|---|---|
|
0000 |
Self-testing or unknown. |
|
0001 |
Firmware update in progress. |
|
0010 |
At least on unsuccessful I/O connection. |
|
0011 |
No I/O connections established. |
|
0100 |
Non-volatile configuration. |
|
0101 |
Major error - either bit 10 or 11 is true. |
|
0110 |
At least one I/O connection in run mode. |
|
0111 |
At least one I/O connection established, all in idle mode. |
|
1000…1001 |
Reserved, set to 0 by default. |
|
1010…1111 |
Vendor or product specific. |
The following table describes the identity services:
|
Service code (hex) |
Supported by |
Service name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Class/Instance |
|
Read all attributes |
|
5 |
Instance |
|
Reset factory default |
|
E |
Class/Instance |
|
Read one attribute |
Message Router Object (Class ID = 02 hex)
The message router provides a message connection that can be used by a client to execute any class or instance services within a physical device.
The following table provides a general overview of the Message Router Object:
|
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 |
Class attributes |
|
1, E |
Class services |
|
1, 2 |
Instance attributes |
|
1, E |
Instance services |
The following table describes the instance attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Get |
STRUCT of UINT |
List of all supported objects |
|
Number of supported classes in class array |
|||
|
ARRAY of UINT |
List of supported class codes |
||
|
2 |
Get |
UINT |
Maximum number of supported connections |
The following table describes the service objects:
|
Service code (hex) |
Supported by |
Service name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Class/Instance |
|
Returns a list of object attributes |
|
E |
Class/Instance |
|
Supplies the contents of the corresponding attribute |
Assembly Object (Class ID = 04 hex)
The assembly object unifies the attributes of various objects and allows data for each object to be transmitted or received using a single connection. The assembly object can be used for input and output data. The direction is considered from the network perspective.
The following table provides a general overview of the assembly object:
|
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1, 2, 3, 6, 7 |
Class attributes |
|
1, E |
Class services |
|
3 |
Instance attributes |
|
E, 10 |
Instance services |
The following table describes the instance attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
3 |
Set |
ARRAY OF BYTE |
Data |
The following table describes the service objects:
|
Service code (hex) |
Supported by |
Service name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
E |
Class/Instance |
|
Supplies the contents of the corresponding attribute |
|
10 |
Instance |
|
Modifies the value of an attribute |
Connection Manager Object (Class ID = 06 hex)
The connection manager object is used for connected and connectionless communication using various subnetworks.
The following table provides a general overview of the connection manager object:
|
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 |
Class attributes |
|
1, E |
Class services |
|
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 |
Instance attributes |
|
1, E, 4E, 52, 54 |
Instance services |
The following table describes the instance attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Set (1) |
UINT |
Number of forward open service requests received. |
|
2 |
Set (1) |
UINT |
Number of forward open service requests which were rejected due to incorrect format. |
|
3 |
Set (1) |
UINT |
Number of forward open service requests which were rejected due to lack of resources. |
|
4 |
Set (1) |
UINT |
Number of forward open service requests that were not rejected due to an invalid format or insufficient resources. |
|
5 |
Set (1) |
UINT |
Number of received forward close service requests. |
|
6 |
Set (1) |
UINT |
Number of forward close service requests which were rejected due to incorrect format. |
|
7 |
Set (1) |
UINT |
Number of forward close service requests which were rejected for reasons other than incorrect format. |
|
8 |
Set |
UINT |
Total number of connection timeouts that have occurred in connections controlled by this connection manager. |
|
(1) A device can refuse the Set request to this attribute if the transmitted attribute value is not zero. In this case, it transmits the general status code 09 hex (invalid attribute value). |
|||
The following table describes the service objects:
|
Service code (hex) |
Supported by |
Service name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Class/Instance |
|
Returns a predefined list of object attributes |
|
E |
Class/Instance |
|
Returns the contents of the corresponding attributes |
|
4E |
Instance |
|
Closes a connection |
|
52 |
Instance |
|
Unconnected transmit service |
|
54 |
Instance |
|
Opens a connection, maximum data size is 511 bytes |
Bus Controller Object (Class ID = 64 hex)
The bus controller object is used to configure all global bus controller parameters. All I/O module parameters are managed individually using the I/O module object.
The following table provides a general overview of the bus controller object:
|
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1, 2 |
Class attributes |
|
E |
Class services |
|
1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 80, 81, E0, E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6 |
Instance attributes |
|
10, 32, 33, 34, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 40, 41, 42, E |
Instance services |
The following table describes the instance attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Get |
UDINT |
Adapter status |
|
2 |
Get |
UINT |
Hardware major revision |
|
3 |
Get |
UINT |
Hardware minor revision |
|
4 |
Get |
UINT |
FPGA hardware revision |
|
5 |
Get |
UINT |
Active boot block |
|
6 |
Get |
UINT |
Default firmware major revision |
|
7 |
Get |
UINT |
Default firmware minor revision |
|
8 |
Get |
UINT |
Update firmware major revision |
|
9 |
Get |
UINT |
Update firmware minor revision |
|
A |
Get |
UINT |
Default FPGA software revision |
|
B |
Get |
UINT |
Update FPGA software revision |
|
20 |
Get |
UINT |
Number of modules |
|
21 |
Get |
UINT |
Length of the analog input data in bytes |
|
22 |
Get |
UINT |
Length of the analog output data in bytes |
|
23 |
Get |
UINT |
Length of the digital input data in bytes |
|
24 |
Get |
UINT |
Length of the digital output data in bytes |
|
25 |
Get |
UINT |
Length of the X2X network status information in bytes |
|
26 |
Get |
UINT |
Length of the output status information in bytes |
|
27 |
Get |
UINT |
Highest X2X station number currently in use |
|
40 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Size of the analog input assembly in bytes (AI) |
|
41 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Size of the analog output assembly in bytes (AO) |
|
42 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Size of the digital input assembly in bytes (DI) |
|
43 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Size of the digital output assembly in bytes (DO) |
|
44 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Size of the X2X network status assembly in bytes (NS) |
|
45 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Size of the output status assembly in bytes (OS) |
|
46 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Composition of the combination input assembly |
|
60 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Global action delay time (ms) |
|
61 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Communication loss (timeout) action |
|
62 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Communication loss (timeout) scope |
|
63 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Communication loss (timeout) reset mode |
|
64 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Program mode (idle) action |
|
65 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Program mode (idle) scope |
|
66 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Action for an inoperable module or a missing module in state “Operational” |
|
67 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Action for missing module(s) during the boot phase |
|
68 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Action for incorrect module type(s) during the boot phase |
|
80 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
X2X Link configuration |
|
81 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
X2X cable length (m) |
|
E0 |
Get |
UINT |
Reading network address switches |
|
E1 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Module initialization delay (ms) |
|
E2 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
Enable/disable the Telnet password |
|
E3 |
Set/Get |
UINT |
IP maximum transmission unit (bytes) |
|
E4 |
Get |
UINT |
Current boot configuration assembly ID |
|
E5 |
Get |
UINT |
Read the number of configured I/O modules |
The following table describes the service objects:
|
Service code (hex) |
Supported by |
Service name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
E |
Class/Instance |
|
Supplies the contents of the corresponding attribute. |
|
10 |
Instance |
|
Modifies the value of an attribute. |
|
32 |
Class/Instance |
– |
Resets any pending timeout. |
|
33 |
Instance |
– |
Saves all system data to flash memory. This permanently stores changes to volatile flash memory that have not been stored there automatically by other services. |
|
34 |
Instance |
– |
Reads any system data from flash memory. This overwrites any changes in RAM with the permanently saved settings. |
|
35 |
Instance |
– |
Deletes the entire flash memory. This restores the default settings. |
|
36 |
Instance |
– |
Reinitializes all assemblies. |
|
37 |
Instance |
– |
Enables one or more extended configuration assemblies. The specified parameter makes it possible to generate several independent figurations in the 10 assemblies. This can be used to enable the desired configuration with the corresponding start assembly ID. All 10 assemblies for a single configuration can also be used. |
|
38 |
Instance |
– |
Clears I/O modules configuration data from RAM. Flash memory is not cleared. |
|
40 |
Instance |
– |
Generates a new configuration based on an existing configuration or the non-connected I/O modules. This includes both configured and non configured I/O modules.
|
|
41 |
Instance |
– |
Clears the parameter list for I/O modules. |
|
42 |
Instance |
– |
Applies the parameter list to existing configurations. This changes all existing configurations. The result is stored in the volatile memory of the RAM. |
Connection Object (Class ID = F4 hex)
The connection object describes the CIP connections present on the device.
The following table provides a general overview of the connection object:
|
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1, 2, 3, 6, 7 |
Class attributes |
|
8, 9 |
Extended class attributes |
|
1, E |
Class services |
|
1, 2, 3, 4, 7 |
Instance attributes |
|
1, E |
Instance services |
The following table describes the extended class attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
8 |
Get |
UINT |
Instance of the connection object that describes the connection object and was used to send this request to the device. |
– |
|
9 |
Get |
ARRAY OF STRUCT |
Array of structures that contain the instances attributes 1 and 2 for each instance. |
(1) |
|
UINT |
Enumerates the connection types. |
Refer to instance attributes below. |
||
|
UINT |
CIP connection number that is linked to this connection. |
Refer to instance attributes below. |
||
|
(1) The index of the array is determined by the instance number, from 1 to the maximum number of instances. The value at index 1 (offset 0) and non-instanced instances set to 0. |
||||
The following table describes the instance attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Get |
UINT |
Enumerates the possible connection types. All connection types with the exception of 0 indicate routing-capable connections of the corresponding type. |
|
|
2 |
Get |
UINT |
CIP connection number that is linked to this connection. This attribute is ignored if the connection type = 0. |
Manufacturer assigns a unique value to identify each communication port. Value 1 is defined for internal product use (i.e. backplane). Value 0 is reserved and cannot be used. |
|
3 |
Get |
STRUCT |
||
|
UINT |
Number of 16-bit words in the following path. |
Range = 2 to 6 |
||
|
Padded EPATH |
Logical path segment that identifies the object for this port. |
The path consists of one logical class segment and one logical instance segment. The maximum size is 12 bytes. |
||
|
4 |
Get |
SHORT_STRING |
Name of the physical network port. |
"Port A", for example. The maximum number of characters is 64. This name must be different for each physical port. If several CIP ports use the same physical port, the same physical name must be used. |
|
7 |
Get |
Padded EPATH |
Rotary switch value |
The switch value identical to attribute 2. |
The following table describes the service objects:
|
Service code (hex) |
Supported by |
Service name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Class/Instance |
|
Returns a predefined list of object attributes. |
|
E |
Class/Instance |
|
Returns the contents of the corresponding attributes. |
TCP/IP Interface Object (Class Code = F5 hex)
The TCP/IP interface object provides a mechanism for configuring the TCP/IP network of the fieldbus interface.
The following table provides a general description of the TCP/IP interface object:
|
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1, 2, 3, 6, 7 |
Class attributes |
|
1, E |
Class services |
|
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 |
Instance attributes |
|
1, 2, E, 10 |
Instance services |
The following table describes the instance attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Get |
DWORD |
|
Refer to interface status table below |
|
2 |
Get |
DWORD |
|
|
|
3 |
Set |
DWORD |
|
|
|
4 |
Get |
STRUCT |
Path to the physically linked object |
The path identifies the object that is connected to the underlying physical communication object. |
|
UINT |
Length of the path |
Number of 16 bits word in the element path. |
||
|
EPATH |
Logical segments that identify the physical link |
The path addresses to the internal port of the built-in 3-port switch. |
||
|
5 |
Get |
STRUCT |
|
Contains TCP/IP configuration parameters. In order to avoid incomplete or incompatible configurations, parameters cannot be set individually. |
|
UDINT |
|
This value is 0 if an IP address has not been configured. Otherwise, a valid class A, B or C address is given. Example: 0164A8C0 hex (corresponds to 192.168.100.1) |
||
|
UDINT |
|
This value is 0 if a network mask has not been configured. Example: 00FFFFFF hex (corresponds to 255.255.255.0) |
||
|
UDINT |
|
This value is 0 if a gateway address has not been configured. Otherwise, a valid class A, B or C address is given. Example: FE64A8C0 hex (corresponds to 192.168.100.254) |
||
|
UDINT |
|
The value 0 indicates that a primary name server has not been configured. Otherwise, a valid class A, B or C address is given. |
||
|
UDINT |
|
The value 0 indicates that a secondary name server has not been configured. Otherwise, a valid class A, B or C address is given. |
||
|
STRING |
|
ASCII characters. The maximum length is 48 characters. They are filled to an even number (filler byte not included in the length). The length is 0 if a domain name has not been configured. |
||
|
6 |
Get |
STRING |
|
ASCII characters. The maximum length is 64 characters. They are filled to an even number (filler byte not included in the length). The length is 0 if a domain name has not been configured. |
The following table provides the interface status of attribute 1:
|
Bit |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0…3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
Indicates a pending configuration change in the TTL value and/or Mcast configuration attribute. This bit is set if either the TTL value or Mcast configuration attribute is set and deleted the next time the device is started. |
|
5…31 |
|
Reserved |
The following table describes the service objects:
|
Service code (hex) |
Supported by |
Service name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Class/Instance |
|
Returns a predefined list of object attributes. |
|
2 |
Instance |
|
Modifies all modifiable attributes. |
|
E |
Class/Instance |
|
Returns the content of the corresponding attributes. |
|
10 |
Instance |
|
Modifies an individual attribute value. |
Ethernet Link Object (Class ID = F6 hex)
The Ethernet link object manages connection-specific counters and status information.
The following table provides a general overview of the Ethernet link object:
|
Value (hex) |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1, 2, 3, 6, 7 |
Class attributes |
|
1, E |
Class services |
|
1, 2, 3 |
Instance attributes |
|
1, E |
Instance services |
The following table describes the instance attributes:
|
Attribute ID (hex) |
Access |
Data type |
Description |
Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Get |
UDINT |
Transfer rate in use |
Speed in Mbps (for instance 0, 10, 100, 1000, etc.) |
|
2 |
Get |
DWORD |
Interface status flag |
Refer to interface status table below |
|
3 |
Get |
ARRAY [0...5] of USINT |
Physical address |
Device-specific MAC address |
The following table describes the status codes of the interface status flag:
|
Bit |
Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
|
Indicates whether the communication interface is connected to an active network.
|
|
1 |
|
Indicates the duplex mode in use.
This flag is undefined if the connection status flag is 0. |
|
2…4 |
|
Indicates the status of auto-negotiation.
|
|
5 |
|
Indicates the change mode required.
|
|
6 |
|
Indicates whether a local error is detected.
|
|
7…31 |
|
Reserved. Set to 0 by default. |
The following table describes the instance service objects:
|
Service code (hex) |
Supported by |
Service name |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Class/Instance |
|
Returns a predefined list of object attributes. |
|
E |
Class/Instance |
|
Provides the contents of the corresponding attribute. |