General Information
Library Overview
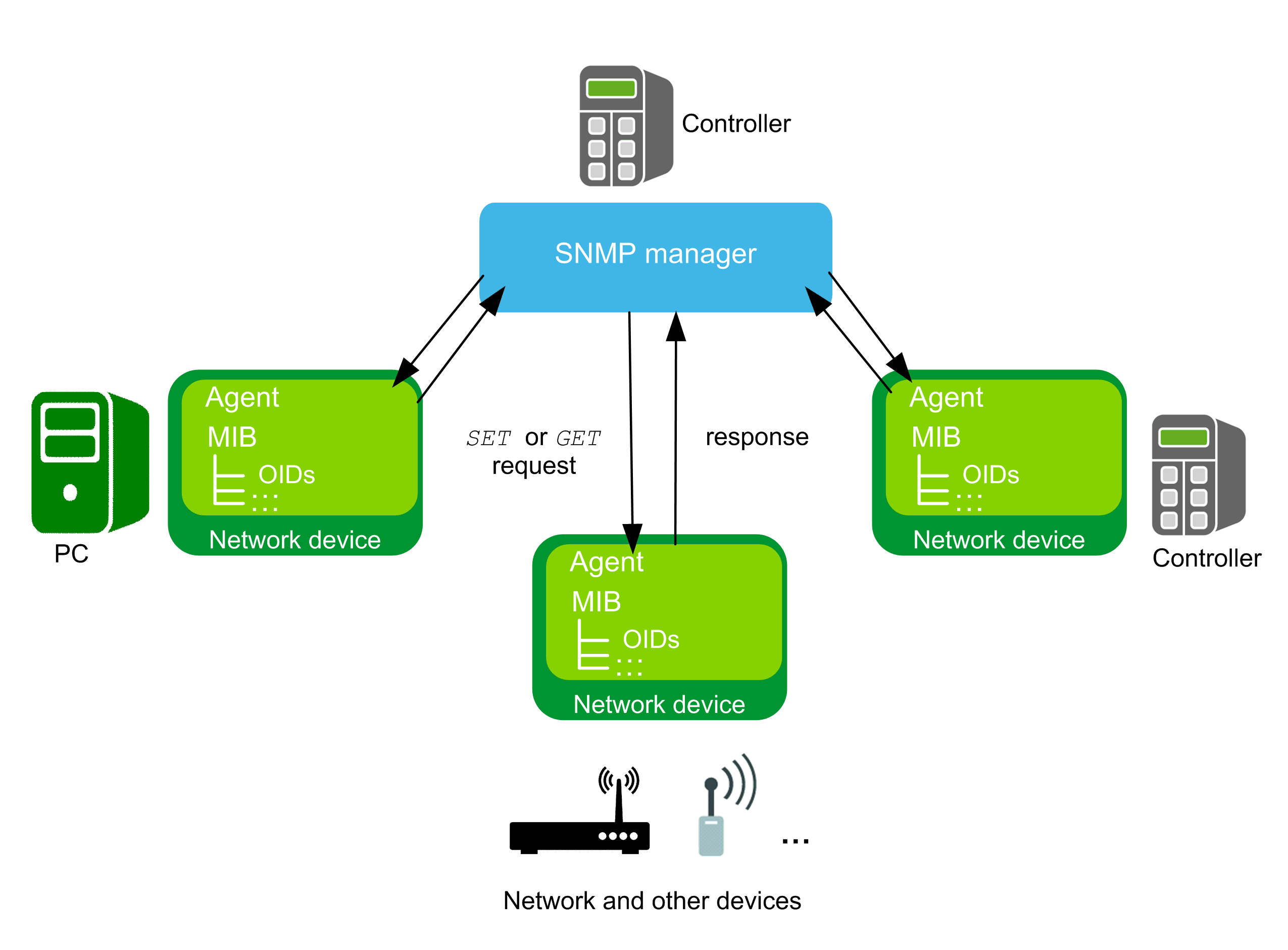
The SnmpManager library implements a manager for the Internet standard protocol SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). The SNMP manager allows your controller to collect and organize information about managed devices on IP (Internet Protocol) networks and to modify this information in order to change the configuration of the device.
The SNMP manager is able to communicate with managed devices over:
-
SNMPv1 protocol as defined in the IETF RFC 1157
-
SNMPv2c protocol (community-based) as defined in the IETF RFC 1901...1907
-
SNMPv3 protocol as defined in the IETF RFC 3412, 3414 and 3826
It provides the following functions:
-
Generating and transmitting a GET request for one Object IDentifier (OID).
-
Generating and transmitting a SET request for one OID.
-
Receiving and structuring the response of the agent.
-
Providing the decoded value from a response in a suitable system type.
-
Encoding a given value for a corresponding SET request.
-
Managing detected errors.
-
Managing authentication requests.
-
Encrypting the Protocol Data Unit (PDU) of a request.
An agent can be any network device providing SNMP functionality such as switches, routers, printers, or other controllers. You must provide the information about the specific Management Information Base (MIB) structure and the corresponding OIDs for each agent.
Characteristics of the Library
The following table indicates the characteristics of the library:
|
Characteristic |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Library title |
SnmpManager |
|
Company |
Schneider Electric |
|
Category |
|
|
Component |
|
|
Default namespace |
|
|
Language model attribute |
|
|
Forward compatible library |
Yes (FCL) |
General Considerations
Consider the following limitations for SNMP communication:
-
Only Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) is supported.
-
Only one request to one SNMP agent is allowed at a time.
-
Only one OID can be processed per request.
-
The SnmpManager library incorporates pointers on addresses.
Executing the command can change the contents of addresses.
| CAUTION | |
|---|---|
The SNMP Manager Library is based on the UDP communications.
The library described in this document internally uses the TcpUdpCommunication library.
The TcpUdpCommunication (Schneider Electric) and the CAA Net Base Services library (CAA Technical Workgroup) use the same system resources on the controller. The simultaneous use of both libraries in the same application may lead to disturbances during the operation of the controller.
| WARNING | |
|---|---|
Considerations Concerning Cybersecurity
The SnmpManager library functions do not support secure connections such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Socket Layer (SSL). Communication must only be performed inside your industrial network, isolated from other networks inside your company, and protected from the Internet.
| WARNING | |
|---|---|
For more information on organizational measures and rules covering access to infrastructures, refer to ISO/IEC 27000 series, Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation, ISO/IEC 15408, IEC 62351, ISA/IEC 62443, NIST Cybersecurity Framework, Information Security Forum - Standard of Good Practice for Information Security and refer to Cybersecurity Guidelines for EcoStruxure Machine Expert, Modicon and PacDrive Controllers and Associated Equipment.