Positioning is a mode where the axis moves to a target undependable of other axis in the application. Below are positioning modes that define the movements and the target.
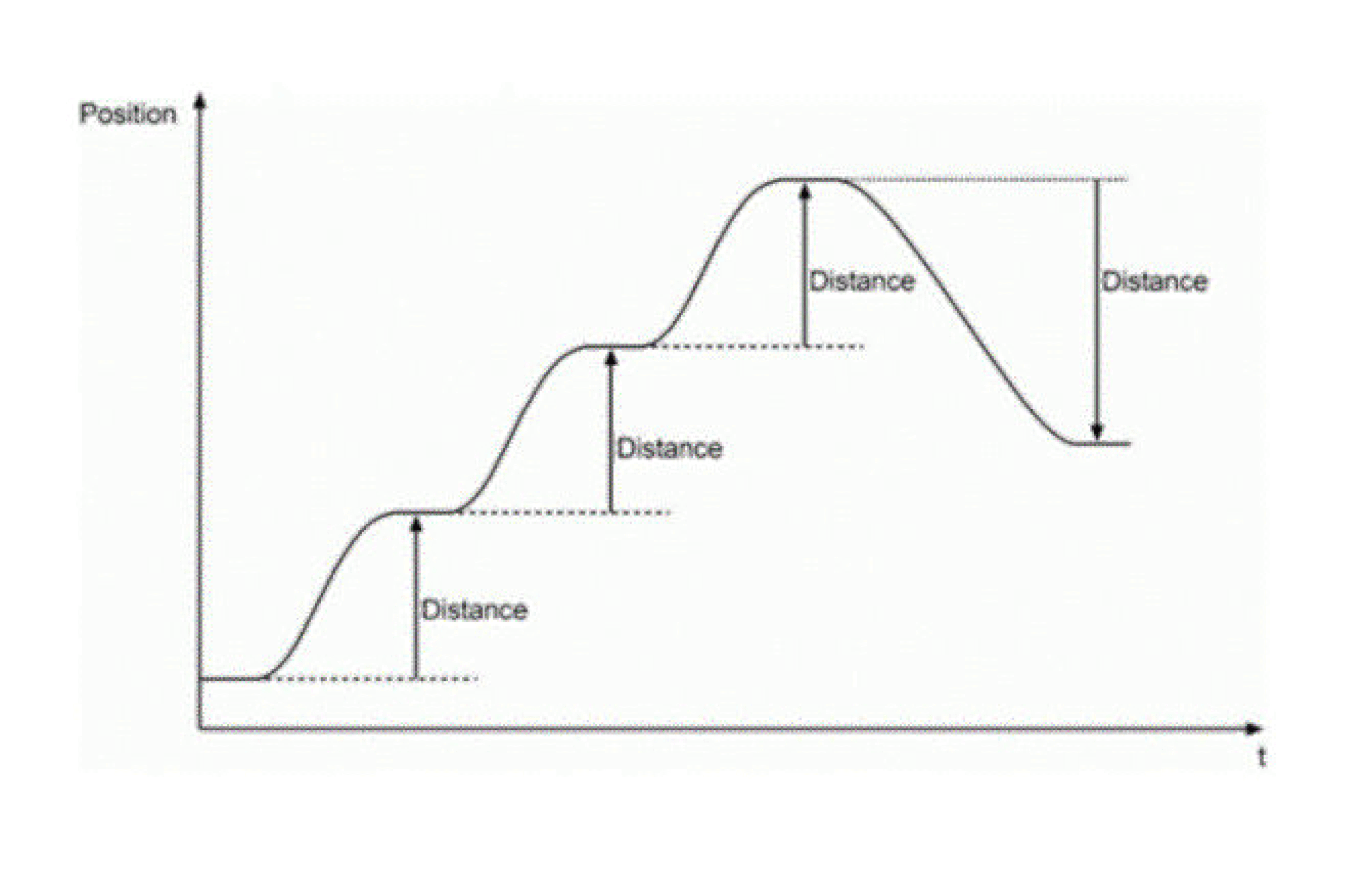
The axis moves the distance of the target and the position of the axis is (starting position + target). Then the movement is done as illustrated in Figure_._.
Relative Trace of the Positioing
The position of the axis is not changed and the movement is (target – starting position). Figure_._ gives an example of Absolute Trace.
Absolute Trace of the Positioning
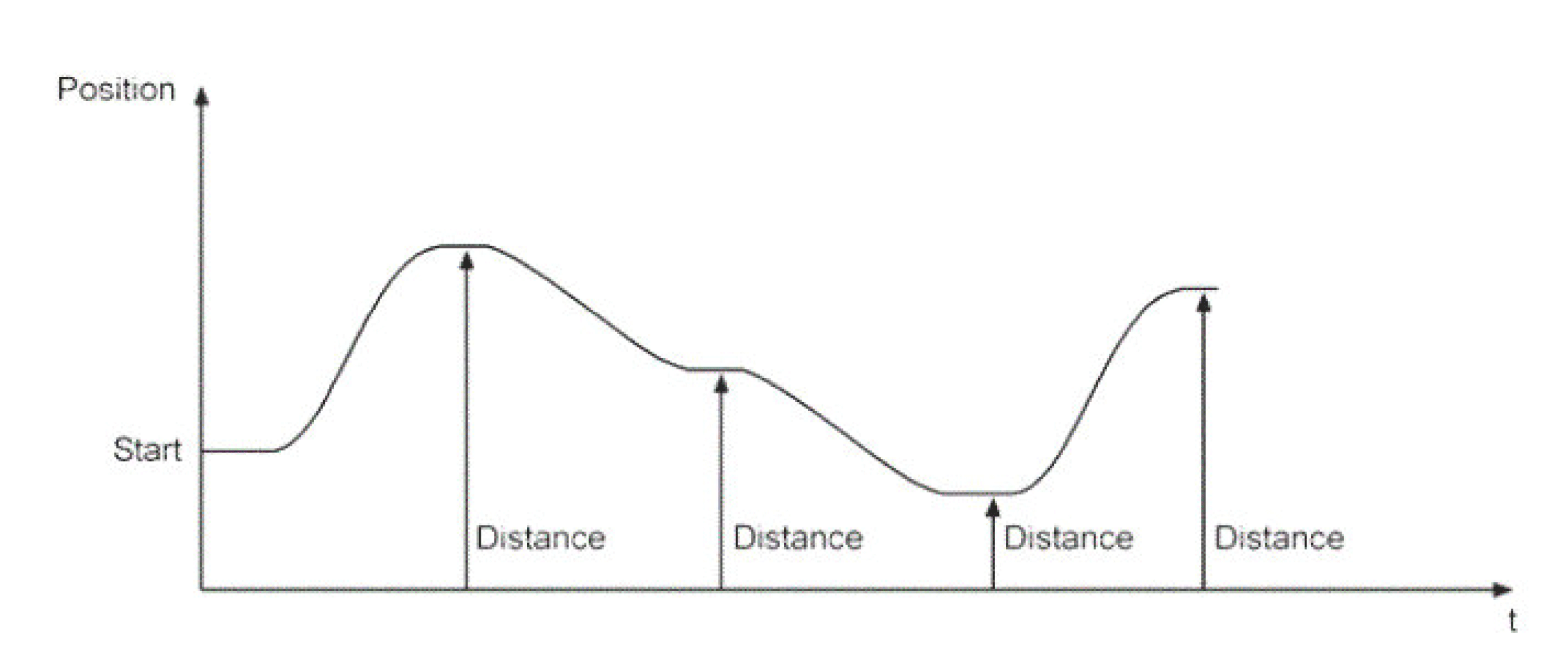
Table __.__ displays a summary of the parameters and the return values of the OpMode_Positioning .
|
Variable |
Data Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
i_etPosMode |
SystemInterface.ET_PosMode |
Positioning mode. SystemInterface.ET_PosMode.Relative SystemInterface.ET_PosMode.Endless SystemInterface.ET_PosMode.Absolute |
|
i_lrTarget |
LREAL |
Travel distance or targets of the motion in the units are dependent on i_etPosMode. |
|
i_lrVel |
LREAL |
Velocity (change of position) in units/s. |
|
i_IrAcc |
LREAL |
Acceleration (change of velocity)in units/s2. |
|
i_lrDec |
LREAL |
Deceleration (change of velocity) in units/s2. |
|
i_lrJerk |
LREAL |
Jerk (change of acceleration/deceleration) in units/s3. |
The Op_Mode Positioning Trace (Figure _._) and source code demonstrate how an axis can be positioned using the given commands:
Positioning Trace Example
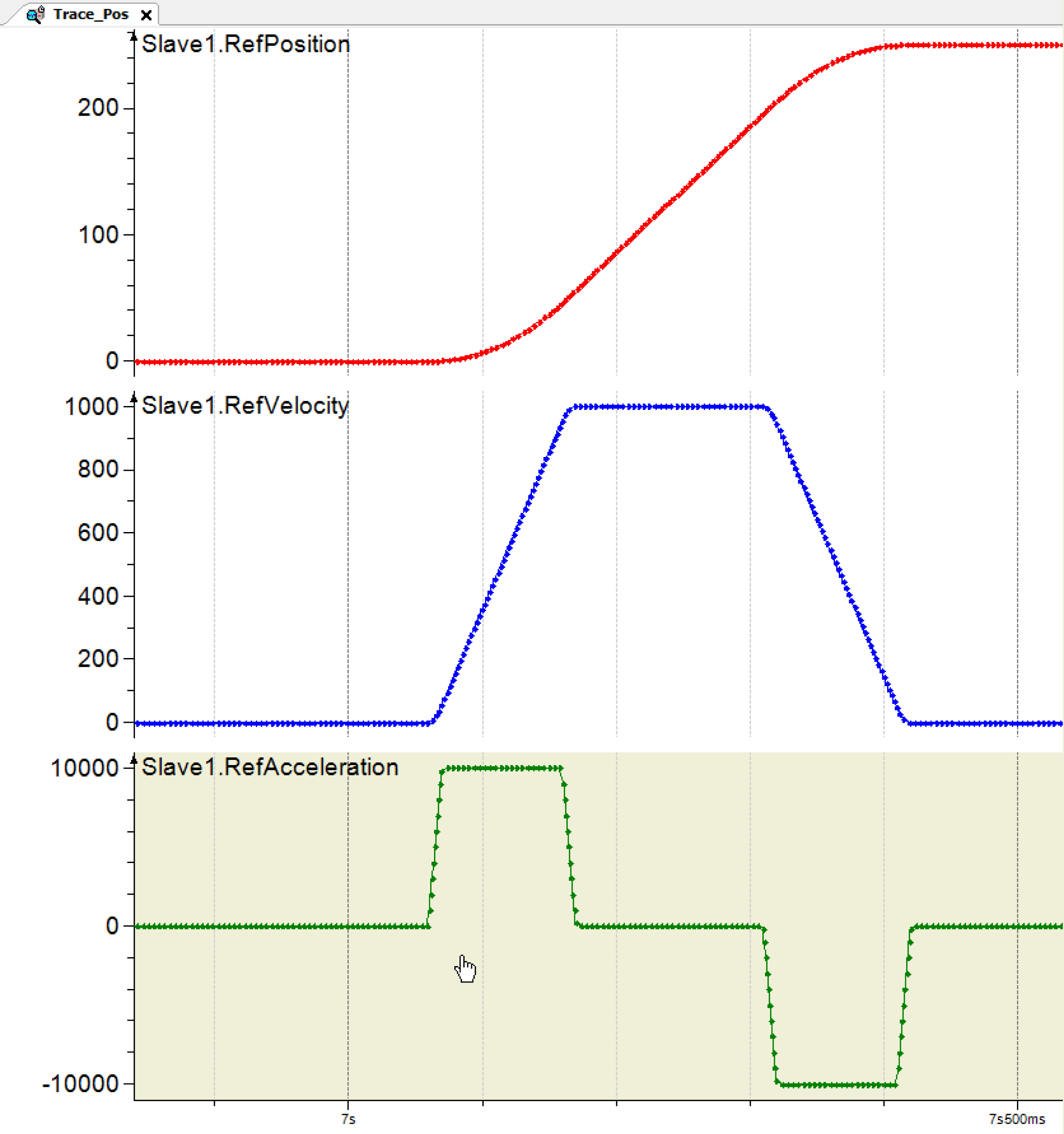
ST_Positioning.i_etPosMode := ET_PosMode.Absolute
ST_Positioning.i_lrTarget := 250.0
ST_Positioning.i_lrVel := 1_000.0
ST_Positioning.i_lrAcc := 10_000.0
ST_Positioning.i_lrDec := 10_000.0
ST_Positioning.i_lrJerk := 1_000_000.0