IDMTL Overcurrent Protection (ANSI 51)
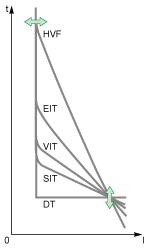
The ANSI 51 – IDMTL overcurrent protection Digital Module provides overcurrent protection based on one of the following IDMTL (Inverse Definite Minimum Time Lag) tripping curves:
oDT: Definite Time curve (constant tripping time)
oSIT: Standard Inverse Time curve (I0.02t)
oVIT: Very Inverse Time curve (It)
oEIT: Extremely Inverse Time curve (I2t)
oHVF: High Voltage Fuse curve (I4t)
The addition of one of the IDMTL tripping curves to the existing long-time overcurrent protection helps to facilitate selectivity with an upstream protection device.
The ANSI 51 – IDMTL overcurrent protection Digital Module can be used to generate either a trip or an alarm.
IDMTL overcurrent protection is available when the ANSI 51 – IDMTL overcurrent protection Digital Module is purchased and installed on a MicroLogic X control unit.
IDMTL overcurrent protection requires an external 24 Vdc power supply or a VPS voltage power supply module.
IDMTL overcurrent protection is compatible with:
oMicroLogic 2.0 X, 5.0 X, 6.0 X, and 7.0 X control units for IEC standard
oMicroLogic 3.0 X, 5.0 X, and 6.0 X control units for UL standard
oMicroLogic X control units with firmware version greater than or equal to 004.000.000. Earlier firmware versions need to be updated.
Data from the Digital Module is available remotely through IFE/EIFE or IFM communication interfaces, if the IFE/EIFE or IFM firmware version is compatible with the Digital Module. For more information, refer to firmware compatibility of the communication interfaces.
NOTE: If the external voltage tap (PTE) option is used with no voltage connected, it is recommended to check that the rated frequency network setting corresponds to the nominal frequency of your electrical network (50 Hz or 60 Hz). For more information, refer to Network Settings.
|
IDMTL overcurrent protection: oIs based on the true RMS current of phases and neutral, up to the 40th harmonic. oHas an adjustable reset time. oIs implemented independently for each phase and the neutral, when neutral is present. oIs an overcurrent time-dependent protection (except when DT (Definite Time) has been selected). oTrips if both the following conditions are met: oThe value of the current exceeds 1.05 x IDMTL Ir setting. oThe calculated tripping time is elapsed. NOTE: When the current is higher than Isd or Ii, only short-time overcurrent protection and instantaneous protection are operational. |
For a time-dependent curve (SIT, VIT, EIT, HVF), the tripping time depends on the current I compared to the IDMTL Ir threshold and the IDMTL tr time delay.
The tripping time (Ttrip) is calculated using the following equation, according to IEC 60255-151 Annex A:
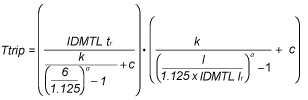
The value of parameters k, c, and α for each tripping curve (SIT, VIT, EIT, HVF) are given in the table below:
|
Tripping curve |
Name |
k |
c |
α |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SIT |
IEC curve type A (inverse) |
0.14 |
0 |
0.02 |
|
VIT |
IEC curve type B (very inverse) |
13.5 |
0 |
1 |
|
EIT |
IEC curve type C (extremely inverse) |
80 |
0 |
2 |
|
HVF |
High voltage fuse |
80 |
0 |
4 |
NOTE: The IDMTL tripping time is always greater than or equal to the short-time overcurrent protection time delay tsd.
If the calculated tripping time according to the equation is lower than tsd, the IDMTL tripping time is forced to the short-time tripping time. In this case, and with I > Isd, the circuit breaker tripping cause can be either IDMTL overcurrent protection or short-time overcurrent protection.
Tripping Time According to IDMTL tr Time Delay
The IDMTL tr overcurrent protection time delay is the tripping time for a phase or neutral current equal to 6 x IDMTL Ir.
The following table indicates the tripping time for the different types of tripping curve, according to the IDMTL tr time delay.
|
IDMTL tr (s) |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tripping curve |
Current I |
Tripping time (s) |
||||||||
|
DT |
1.5 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
6 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
|
7.2 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
|
10 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
|
SIT |
1.5 x IDMTL Ir |
3 |
5.9 |
11.8 |
23.6 |
47.2 |
70.8 |
94.4 |
118 |
142 |
|
6 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
|
7.2 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
0.9 |
1.8 |
3.6 |
7.2 |
10.8 |
14.4 |
18 |
21.6 |
|
|
10 x IDMTL Ir |
0.4 |
0.8 |
1.5 |
3 |
6.1 |
9.1 |
12.2 |
15.2 |
18.3 |
|
|
VIT |
1.5 x IDMTL Ir |
6.5 |
13 |
26 |
52 |
104 |
156 |
208 |
260 |
312 |
|
6 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
1.0 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
|
7.2 x IDMTL Ir |
0.4 |
0.8 |
1.6 |
3.2 |
6.4 |
9.6 |
12.8 |
16 |
19.3 |
|
|
10 x IDMTL Ir |
0.3(1) |
0.5 |
1.1 |
2.2 |
4.4 |
6.6 |
8.8 |
11 |
13.2 |
|
|
EIT |
1.5 x IDMTL Ir |
17.6 |
35.3 |
70.6 |
141 |
282 |
423 |
565 |
706 |
847 |
|
6 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
|
7.2 x IDMTL Ir |
0.3(1) |
0.7 |
1.4 |
2.7 |
5.5 |
8.2 |
11 |
13.7 |
16.5 |
|
|
10 x IDMTL Ir |
0.2(1) |
0.4 |
0.7 |
1.4 |
2.8 |
4.2 |
5.6 |
7 |
8.4 |
|
|
HVF |
1.5 x IDMTL Ir |
187 |
374 |
748 |
1496 |
2992 |
4488 |
5984 |
7481 |
8977 |
|
6 x IDMTL Ir |
0.5 |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
|
|
7.2 x IDMTL Ir |
0.2(1) |
0.5 |
1 |
1.9 |
3.9 |
5.8 |
7.7 |
9.6 |
11.6 |
|
|
10 x IDMTL Ir |
0.1(1) |
0.1(1) |
0.3(1) |
0.5 |
1 |
1.6 |
2.1 |
2.6 |
3.1 |
|
|
(1) When the calculated tripping time is lower than tsd, the IDMTL tripping time is forced to the short-time tripping time. |
||||||||||
An adjustable reset time helps to improve protection in the case of intermittent overcurrents. The reset time of a protection function is the time between the end of the overcurrent detection and the reset of the protection time delay.
The reset time of IDMTL overcurrent protection starts when I ≤ 1.125 x IDMTL Ir.
The following graphic illustrates the operation of definite reset time for different types of overcurrent:
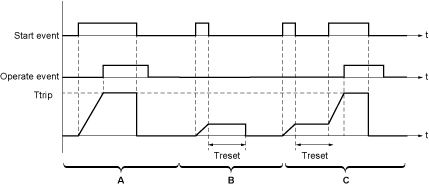
A Permanent overcurrent
B Transient overcurrent
C Intermittent overcurrent
The reset time of IDMTL overcurrent protection is adjustable and has the following types:
oReset time with definite time curve.
This can be used in the case of intermittent overcurrents. The time to reset is fixed: Treset = IDMTL reset time.
oReset time with inverse time curve.
This can be used in the case of intermittent overcurrents and functions in a similar way to the thermal memory of long-time overcurrent protection. The time to reset (Treset) is calculated according to the following equation:
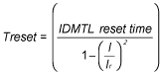
To inhibit the IDMTL overcurrent protection, both the following conditions must be met:
oInhibition is enabled by setting the Inhibition parameter to ON.
oInhibition of optional protections is activated by an input of the IO module. The function to Inhibit Optional Protection must be assigned to an input of the IO module.
For more information about inhibiting optional protections, refer to Enerlin'X IO - Input/Output Application Module for One Circuit Breaker - User Guide.
The IDMTL overcurrent protection settings are:
oIDMTL mode: enables (ON) or disables (OFF) the protection
oIDMTL action: sets the result of the protection as trip or alarm
oIDMTL inhib: enables (ON) the protection to be inhibited by IO module
oIDMTL Ir: IDMTL overcurrent protection threshold
oIDMTL tr: IDMTL overcurrent protection time delay
oIDMTL curve: selects the type of IDMTL tripping curve (DT, SIT, VIT, EIT, HVF)
oIDMTL reset time type: selects the reset time type as definite time or inverse time
oIDMTL reset time
They can be set as follows:
oWith EcoStruxure Power Commission software (password-protected)
oWith EcoStruxure Power Device app (password-protected)
The dual settings function does not apply to IDMTL overcurrent protection. When the dual settings function is enabled, IDMTL overcurrent protection settings are the same whether set A or set B settings are activated.
NOTE: Long-time overcurrent protection (ANSI 49RMS/51) remains active when IDMTL overcurrent protection (ANSI 51) is configured. For recommendations on how to maintain consistency between settings, refer to the setting guidelines.
|
Setting |
Unit |
Setting range |
Step |
Factory setting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IDMTL mode |
– |
ON/OFF |
– |
OFF |
|
IDMTL action |
– |
Alarm/Trip |
– |
Alarm |
|
IDMTL inhibit |
– |
ON/OFF |
– |
OFF |
|
IDMTL Ir |
A |
0.4 –1.5 x In |
1 |
In |
|
IDMTL tr |
s |
0.1–24 |
0.1 |
1 |
|
IDMTL curve |
– |
DT/SIT/VIT/EIT/HVF |
– |
EIT |
|
IDMTL reset time type |
– |
Definite time/Inverse time |
– |
Definite time |
|
IDMTL reset time |
s |
0–10 |
0.1 |
0.5 |
For more information, refer to the setting guidelines.
The accuracy of IDMTL Ir is ± 5%
Characteristics of IDMTL overcurrent protection:
oTime-dependent delay (except when DT selected)
oReset time: adjustable
IDMTL Ir characteristics:
oI < 1.05 x IDMTL Ir: no trip
oI > 1.2 x IDMTL Ir: trip
The function generates the following predefined events:
|
Code |
Event |
History |
Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0x6421 (25633) |
IDMTL long time trip |
Trip |
High |
|
0x6221 (25121) |
IDMTL long time start |
Protection |
Medium |
|
0x6321 (25377) |
IDMTL long time operate |
Protection |
Medium |
|
0x0EF8 (3832) |
Optional protection inhibited by IO module |
Protection |
Low |
|
0x0D0C (3340) |
Config error IO/CU: optional protection Inhibit |
Configuration |
Medium |
Predefined events cannot be modified by the user. For general information about events, refer to Event management.
Protection events are generated as follows:
oThe start event is generated when the protection picks up.
oThe operate event is generated when the protection time delay elapses.
The operate event is not generated when the optional protection is inhibited.
oThe trip event is generated when the circuit breaker tripping voltage release (MITOP) activates.
The trip event is not generated when:
oThe optional protection is set in alarm mode
oThe optional protection is inhibited
|
Code |
Event |
Recommended actions |
|---|---|---|
|
0x6421 (25633) |
IDMTL long time trip |
Reset the device or use the Power restoration assistant within the EcoStruxure Power Device app. |
|
0x0EF8 (3832) |
Optional protection inhibited by IO module |
Check inhibition selector switch wired with IO module. |
|
0x0D0C (3340) |
Config error IO/CU: optional protection Inhibit |
Correct the configuration error with EcoStruxure Power Commission software: oIf you want optional protection inhibition to be controlled by IO module, connect an IO module with inhibit optional protection assignment. oIf you do not want optional protection inhibition to be controlled by IO module, connect an IO module without inhibit optional protection assignment. |
For information about resetting the circuit breaker after a trip due to an electrical fault, refer to the relevant document:
oMasterPact MTZ1 - Circuit Breakers and Switch-Disconnectors - User Guide
oMasterPact MTZ2/MTZ3 - Circuit Breakers and Switch-Disconnectors - User Guide