Cybersecurity Admin Expert
Cybersecurity Admin Expert (CAE) is a software tool used to configure and apply security settings to a device in a network of industrial control systems. Devices can include switches, firewalls, PCs, and IED/Protection relays.
Devices must be CTI023 compliant or have a Digital Power CS brick, a cybersecurity brick embedded inside that enables it to communicate with CAE.
Using CAE with EcoStruxure Power Operation is optional.
CAE has security capabilities that help:
- Protect the confidentiality of information.
- Align with NERC CIP reliability standards and IEC 62443 international standards.
- Protect the device from unauthorized configuration security changes.
- Enforce authorizations assigned to users, segregation of duties, and least privilege.
- Prohibit and restrict the use of unnecessary functions, ports, protocols, or services.
CAE architecture
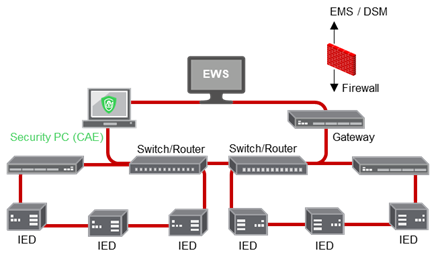
Encryption
CAE manages the encryption of data exchanged through some communication channels. CAE helps protect configuration and process data from any corruption, malice, or attack.
Hardening
Observe the following recommendations to optimize cybersecurity in a protected environment:
- Harden devices according to your company’s policies and standards.
- Apply and maintain the CAE security capabilities.
- Use an antivirus software and implement updates for the operating system and Microsoft .NET Framework on the machine dedicated to CAE tool.
- Follow user account management tasks as described by your organization or contact your network administrator.
 warning
warning
potential compromise of System availability, integrity, and confidentiality
-
Change default passwords to help prevent unauthorized access to settings and information.
-
Use Windows Active Directory for user account management and access to network resources.
-
Disable unused ports/services and default accounts, where possible, to minimize pathways for malicious attacks.
-
Place networked devices behind multiple layers of cyber defenses (such as firewalls, network segmentation, and network intrusion detection and protection).
-
Use cybersecurity best practices (for example: least privilege, separation of duties) to help prevent unauthorized exposure, loss, modification of data and logs, interruption of services, or unintended operation.
-
Follow cybersecurity tasks as described by your organization or contact your network administrator.
Failure to follow these instructions can result in death, serious injury, equipment damage, or permanent loss of data.