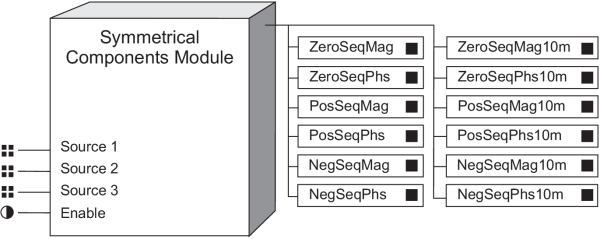
Symmetrical Components Module
The Symmetrical Components Module provides information about unbalanced voltages and currents in a polyphase power system.
Module icon
![]()
Overview
The information provided by this module allows you to identify or predict how electrical equipment might be affected. For example, some possible applications include reducing induced, circulating currents in motor windings, or preventing equipment damage, or even prolonging motor and transformer life. The Symmetrical Components Module calculates the magnitude and phase angle of zero, positive and negative sequences of the fundamental components for either voltage or current.
NOTE: The registers and settings available in this module depend on the device you are configuring, as well as its firmware and template versions. Not all registers or settings are available on all devices, and labels may vary.
Inputs
 Source 1, Source 2, Source 3
Source 1, Source 2, Source 3
The Source inputs of the Symmetrical Components modules are fixed to the outputs of either voltage or current FFT modules.
 Enable
Enable
The Enable input is factory-linked and cannot be altered.
Setup registers
This module has no setup registers.
Output registers
 ZeroSeqMag (zero sequence magnitude)
ZeroSeqMag (zero sequence magnitude)
This register contains the zero sequence magnitude. On a meter that is 4-30 compliant, it will represent the aggregation over 150/180 cycles.
 ZeroSeqPhs (zero sequence phase angle)
ZeroSeqPhs (zero sequence phase angle)
This register contains the zero sequence phase angle. On a meter that is 4-30 compliant, it will represent the aggregation over 150/180 cycles.
 PosSeqMag (positive sequence magnitude)
PosSeqMag (positive sequence magnitude)
This register contains the positive sequence magnitude. On a meter that is 4-30 compliant, it will represent the aggregation over 150/180 cycles.
 PosSeqPhs (positive sequence phase angle)
PosSeqPhs (positive sequence phase angle)
This register contains the positive sequence phase angle. On a meter that is 4-30 compliant, it will represent the aggregation over 150/180 cycles.
 NegSeqMag (negative sequence magnitude)
NegSeqMag (negative sequence magnitude)
This register contains the negative sequence magnitude. On a meter that is 4-30 compliant, it will represent the aggregation over 150/180 cycles.
 NegSeqPhs (negative sequence phase angle)
NegSeqPhs (negative sequence phase angle)
This register contains the negative sequence phase angle. On a meter that is 4-30 compliant, it will represent the aggregation over 150/180 cycles.
 ZeroSeqMag10m (zero sequence magnitude)
ZeroSeqMag10m (zero sequence magnitude)
This register contains the zero sequence magnitude, aggregated over a ten-minute harmonics interval. It is updated at the end of the interval. On a meter that is not 4-30 compliant, this register is not used.
 ZeroSeqPhs10m (zero sequence phase angle)
ZeroSeqPhs10m (zero sequence phase angle)
This register contains the zero sequence phase angle, aggregated over a ten-minute harmonics interval. It is updated at the end of the interval. On a meter that is not 4-30 compliant, this register is not used.
 PosSeqMag10m (positive sequence magnitude)
PosSeqMag10m (positive sequence magnitude)
This register contains the positive sequence magnitude, aggregated over a ten-minute harmonics interval. It is updated at the end of the interval. On a meter that is not 4-30 compliant, this register is not used.
 PosSeqPhs10m (positive sequence phase angle)
PosSeqPhs10m (positive sequence phase angle)
This register contains the positive sequence phase angle, aggregated over a ten-minute harmonics interval. It is updated at the end of the interval. On a meter that is not 4-30 compliant, this register is not used.
 NegSeqMag10m (negative sequence magnitude)
NegSeqMag10m (negative sequence magnitude)
This register contains the negative sequence magnitude, aggregated over a ten-minute harmonics interval. It is updated at the end of the interval. On a meter that is not 4-30 compliant, this register is not used.
 NegSeqPhs10m (negative sequence phase angle)
NegSeqPhs10m (negative sequence phase angle)
This register contains the negative sequence phase angle, aggregated over a ten-minute harmonics interval. It is updated at the end of the interval. On a meter that is not 4-30 compliant, this register is not used.
Responses to special conditions
The following table summarizes how the module behaves under different conditions.
|
Condition |
Response of output registers |
|---|---|
|
When the device is started or powered-up (either the first time, or after a shutdown) |
All output registers are not available. |
|
If the inputs are not available |
All output registers are not available. |
|
If the Enable input is off |
All output registers are not available. |
Detailed module operation
Ideally in a polyphase power system, phases A, B, and C of voltage and current are equal in magnitude, separated by 120°, and have a particular rotation. When this is not the case, the system is unbalanced and power use is inefficient.
For example, when unbalanced power is applied to a motor, some of the power contributes to turning the motor in the proper direction (positive sequences), some of the power may contribute to the motor actually turning backwards (negative sequences), and some of the power may just cause heating (zero sequences). The Symmetrical Components module analyzes the unbalance and determines the magnitudes and phase angles of the positive, negative and zero sequences. These values are stored in the output registers.